Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-121102-15
- Publication
- Sager et al., 2012 - The Zebrafish Homologue of the Human DYT1 Dystonia Gene Is Widely Expressed in CNS Neurons but Non-Essential for Early Motor System Development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
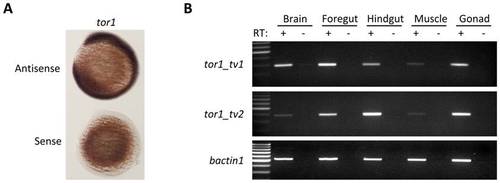
tor1 is expressed ubiquitously. A: RNA in situ hybridization was employed to detect the tor1 transcript during development. Hybridized probe was detected using a histochemical reaction with a blue/purple product. The photomicrograph shows embryos at 12 hpf; the upper of the pair was hybridized with a tor1 antisense probe and the lower with a tor1 sense control probe. B: Reverse transcriptase PCR was employed to detect tor1_tv1 (upper panel) or tor1_tv2 (middle panel) mRNA in brain, foregut, hindgut, muscle, and gonads of adult zebrafish. Total RNA was treated with reverse transcriptase (RT+); controls lacking reverse transcriptase (RT-) excluded amplification of genomic DNA sequences. bactin1 was amplified as a ubiquitously expressed control mRNA (lower panel). |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | 5-9 somites to Adult |