Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-120824-1
- Publication
- Kindt et al., 2012 - Kinocilia mediate mechanosensitivity in developing zebrafish hair cells
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
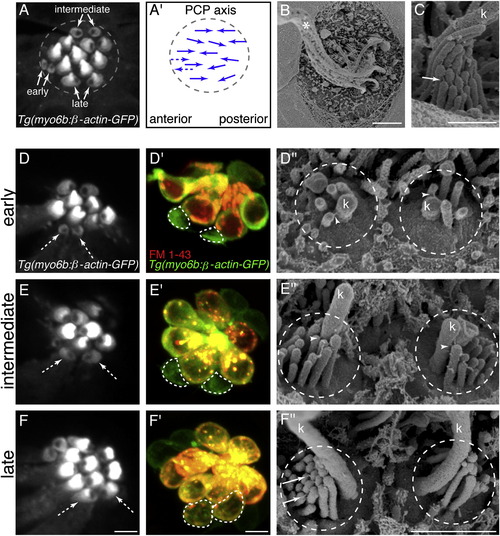
Direct Comparison of Hair-Bundle Development Using Transgenic β-actin-GFP, FM 1-43, and SEM(A) Top-down view of neuromast hair bundles labeled with Tg(myo6b:β-actin-GFP). Three stages of immature hair-bundle development can be observed: early, intermediate, and late. The unlabeled region on either the caudal or rostral side of each bundle is the insertion point of the kinocilium.(A2) Arrows indicate planar polarity and functional polarity of hair bundles in (A). Dashed arrows indicate predicted planar polarity. PCP, planar cell polarity.(B) SEM image of a neuromast at 3 dpf; asterisk denotes the many tall kinocilia (k).(C) SEM image of a mature hair bundle.(D, E, and F) Confocal images of hair bundles expressing β-actin-GFP. White dashed arrows indicate hair bundles of respective stage examined.(D′, E′, and F′) White dashed lines outline cell bodies after FM 1-43 label of hair bundle examined in (D), (E), and (F).(D′′, E′′, and F′′) SEM images of hair bundles in (D), (E), and (F). All images were taken at 3 dpf. White arrowheads denote kinocilial links; solid white arrows denote tip links. Anterior is left; dorsal is up. Scale bars, 2.5 μm (A, B, D, E and F), 500 nm (C), 5 μm (D′, E′, and F′), and 1 μm (D′′, E′′, and F′′). See also Figure S1. |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 23(2), Kindt, K.S., Finch, G., and Nicolson, T., Kinocilia mediate mechanosensitivity in developing zebrafish hair cells, 329-341, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell