Fig. 1
|
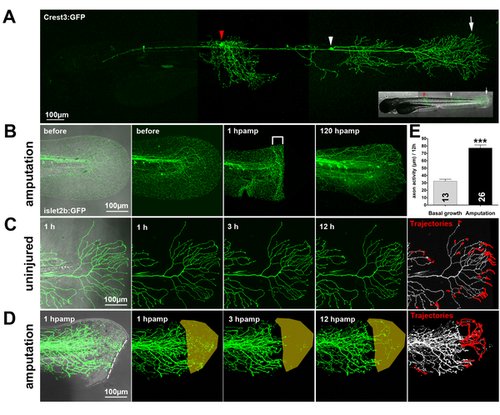
(A) A transient transgenic larva expressing GFP in two RB neurons: one innervating the trunk (red arrowhead) and one innervating the tail fin (white arrowhead). Arrow indicates the RB peripheral arbor in the tail fin. (B) Fin amputation in a 78 hpf islet2b:GFP transgenic larva caused severed axon branches to degenerate at the wound margin (brackets, 1 h post-amputation [hpamp]). RB axon arbors completely reinnervated the regenerated fin by 120 hpamp. (C, D) Time-lapse sequences from 78–90 hpf. The rightmost panel shows axon tip trajectories (red) over the course of the time-lapse (see also Video S1 for a tracing example). (C) The branches of a single GFP-labeled peripheral axon in an uninjured fin underwent minimal growth and retraction. Some of this apparent activity was due to movement of the tissue during time-lapse (see Video S1). (D) Fin amputation (dotted line) increased the growth of the severed arbor (see also Figure 3D, E) and promoted reinnervation of denervated territory (shaded area) (Video S3). (E) Quantification of axon activity in uninjured fins (n = 13) and after fin amputation (n = 26) (two-tailed, unpaired Student′s t-test, *** p<0.001). Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. hpamp, hours post amputation. |