|
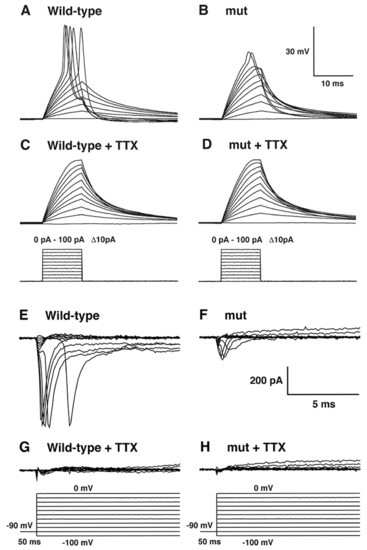
Mutant RB neurons fail to generate normal action potentials owing to defective sodium currents. (A) Injection of step currents up to 100 pA elicited typically large action potentials in a wild-type RB neuron. (B) Current injection into a mutant RB cell failed to generate normal action potentials. (C) The spikes in wild-type RB neurons were eliminated by bath application of TTX, a sodium channel blocker. (D) The small, partial spikes in mutant RB neurons were also eliminated by TTX. (E) Inward sodium currents elicited by voltage steps from -100 mV to 0 mV were recorded in wild-type RB neurons. (F) Inward sodium currents in mutant RB neurons were observed but with smaller amplitude than those seen in wild-type neurons. (G) The inward sodium currents in wild type were blocked in the presence of TTX. (H) The sodium currents in mutant RB cells were also eliminated by TTX.
|