Fig. S2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-090617-28
- Publication
- Nagy et al., 2009 - Endothelial cells promote migration and proliferation of enteric neural crest cells via beta1 integrin signaling
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
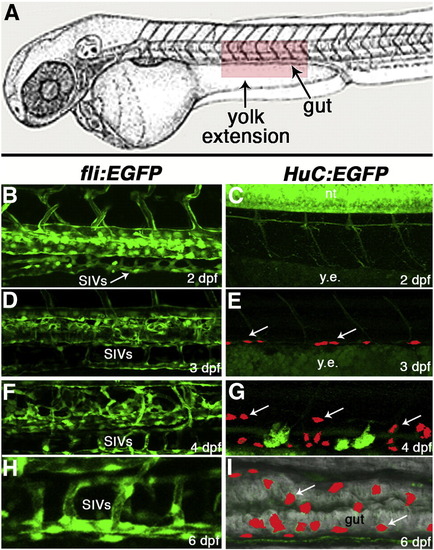
Subintestinal vessels (SIVs) form ahead of enteric neurons in zebrafish embryos. (A) Diagram of a zebrafish embryo with red box depicting the approximate area of the yolk extension, gut, and trunk imaged in panels B-I. Confocal images of corresponding areas of fli:EGFP (B,D,F,H) and HuC:EGFP (C,E,G,I) transgenic embryos at the same stages of development. At 2 dpf, the subintestinal vascular network is seen along the yolk extension (B, arrow), whereas no enteric neurons are detected in this area at the same developmental stage (C). At 3 dpf, a few enteric neurons (E, arrow) have reached the dorsal aspect of the yolk extension. At 4 dpf (F,G) and 6 dpf (H,I), larger numbers of neurons have arrived, and the SIVs and ENS cells now surround a well-formed intestine. In panels E,G,I, confocal stacks were used to specifically identify ENCC-derived GFP signal in the background of green yolk autofluorescence. Hu-labeled cells were then manually colored red in reconstructed images to facilitate visualization. dpf, days post-fertilization; y.e., yolk extension; SIVs, subintestinal vessels. The image in panel A is modified from (Kimmel et al., 1995). |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 330(2), Nagy, N., Mwizerwa, O., Yaniv, K., Carmel, L., Pieretti-Vanmarcke, R., Weinstein, B.M., and Goldstein, A.M., Endothelial cells promote migration and proliferation of enteric neural crest cells via beta1 integrin signaling, 263-272, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.