Fig. S3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-090617-26
- Publication
- Zhang et al., 2009 - Transient and transgenic analysis of the zebrafish ventricular myosin heavy chain (vmhc) promoter: An inhibitory mechanism of ventricle-specific gene expression
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
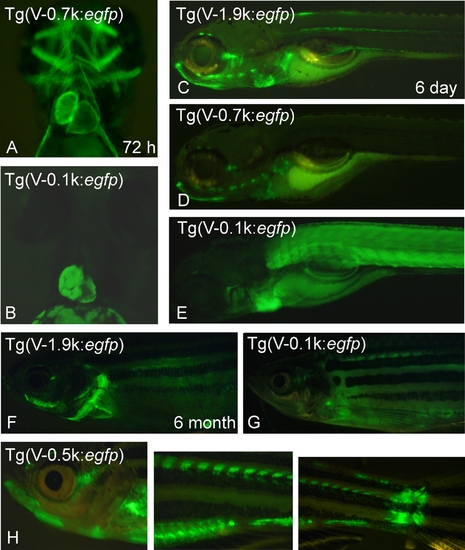
Transgenic fish also express GFP in different muscles. A,B: Tg(V-0.7k:egfp) embryos at 72 hpf exhibited an early onset and strong GFP expression in the extraocular and pharyngeal muscles (A), while Tg(V-0.1k:egfp) embryos did not (B). C-E: Day-6 larval fish from different transgenic lines express GFP in multiple muscles. Similar to Tg(V-0.7k:egfp) fish expressing GFP in the extraocular muscles, pharyngeal muscles, and fin musculature (D), Tg(V-1.9k:egfp) fish also express GFP in myocytes in the body midline (C). In contrast, Tg(V-0.1k:egfp) fish display very weak GFP expression in the cephalic musculature, but strong expression in trunk muscles (E). F-H: Adult 6-month-old fish from different transgenic lines also exhibit varied GFP expression patterns. Most lines have strong (F, H) or weak (G) GFP expression around the eye, jaw, and on the operculum. Muscles near the pectoral and tail fins frequently show GFP signals, as do the dorsal, ventral, and anal fins (H). |