Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080828-89
- Publication
- Douglass et al., 2008 - Escape behavior elicited by single, channelrhodopsin-2-evoked spikes in zebrafish somatosensory neurons
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
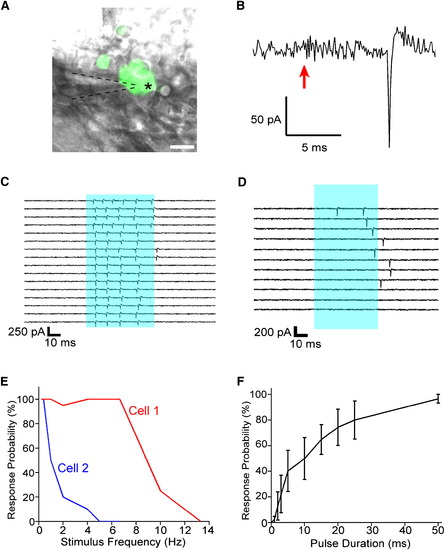
Extracellular Recording of ChR2-Evoked Spiking Activity in Trigeminal Neurons (A) Loose-patch recordings were made by targeting GFP-positive cells (asterisk) with a glass microelectrode (dashed lines) and forming a loose seal of ∼50–100 MΩ. The scale bar represents 20 μm. (B) Current traces from ChR2-expressing neurons showed light-evoked spikes occurring after stimulus onset (arrow). (C) Prolonged stimuli of 50 ms trigger repetitive firing. Sixteen stimuli of 50 ms (blue bar) were delivered to the target cell at 0.2 Hz. (D) Failures occur more often with high-frequency stimulation and after many stimulus repetitions. Light pulses of 50 ms (blue bar) were delivered at 1 Hz for 100 s; every tenth trial in the series is shown. (E) The dependence of failure rate on stimulation frequency varies between cells. Two neurons in two fish were exposed to 20x 50 ms pulses at varying frequencies, and the probability of showing one or more spikes per stimulus was plotted as a function of frequency. (F) Response probability increases with pulse duration (n = 9). Data are mean ± SEM. |