Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080424-74
- Publication
- Kawahara et al., 2002 - The homeobox gene mbx is involved in eye and tectum development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
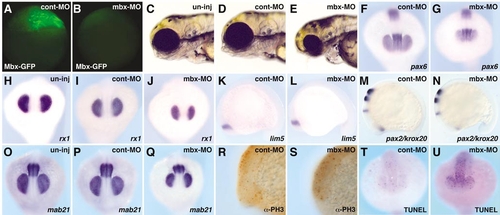
mbx knockdown phenotype with morpholino oligonucleotides. (C, H, O) Uninjected embryos; (A, D, F, I, K, M, P, R, T) cont-MO (5 ng)-injected embryos; (B, E, G, J, L, N, Q, S, U) mbx-MO (5 ng)-injected embryos. (A, B) Mbx-GFP expression at the sphere stage; lateral view. Mbx-GFP RNA (0.5 ng) was injected into the blastomere at the one-cell stage and either mbx-MO or cont-MO was injected into the yolk region. Mbx-GFP expression was suppressed in mbx-MO-injected embryos (B), but not in cont-MO-injected embryos (A). (C–E) Live embryos at 3 dpf: lateral view. Injection of mbx-MO, but not cont-MO, led to a reduction of eye size. (F–Q) Whole-mount in situ hybridization with probes shown at the bottom of each panel at the 15-somite stage. (F–J, O–Q) Anterior view. (K–N) Lateral view. Mbx-MO injection led to a smaller eye field visualized with rx1, mab21l2 and pax6 (F–J, O–Q), and a smaller tectal domain visualized by mab21l2 (O–Q). Expression of pax6 and lim5 (diencephalon: F, G, K, L), pax2.1 (optic stalk and MHB: M, N), and krox20 (hindbrain: M, N) are similar in cont-MO- and mbx-MO-injected embryos. (R, S) Anti-phosphohistone H3 antibody, visualizing mitotic cells, stains similar numbers of cells in cont-MO- and mbx-MO-injected embryos. (T, U) TUNEL assay indicates an increased number of apoptotic cells in mbx-MOinjected embryos. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 248(1), Kawahara, A., Chien, C.-B., and Dawid, I.B., The homeobox gene mbx is involved in eye and tectum development, 107-117, Copyright (2002) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.