Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080417-36
- Publication
- Cooper et al., 2003 - Autonomous and nonautonomous functions for Hox/Pbx in branchiomotor neuron development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
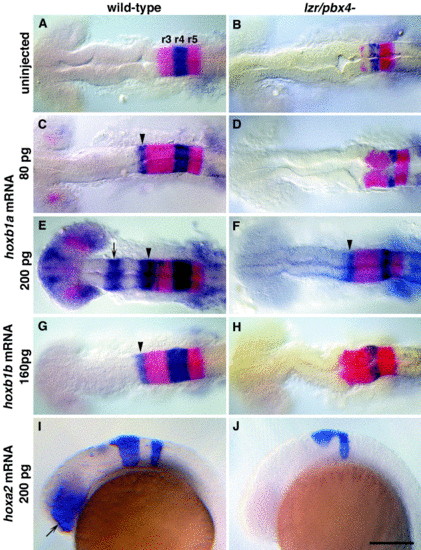
lazarus/pbx4 is required for the ectopic effects of hoxb1a, hoxb1b, and hoxa2. RNA in situ hybridization with krox20 (red in A–H, blue in I, J) and hoxb1a (blue in A–H) on wild-type (left column) and lzr/pbx4-/- (right column) embryos treated as shown. (A, B) In uninjected embryos, krox20 is expressed in r3 and r5, and hoxb1a is expressed in r4. In lzr/pbx4-/- embryos, krox20 expression in r3 and hoxb1a expression in r4 are reduced. (C–F) The effects of ectopically expressing hoxb1a at 80 (C, D) and 200 pg (E, F) are suppressed in lzr/pbx4-/- embryos. Arrowheads and arrows indicate ectopic endogenous hoxb1a expression in r2 and in the midbrain, respectively. (G, H) Similarly, the effects of over-expressing hoxb1b at about 160 pg are suppressed in lzr/pbx4-/- embryos. (I, J) Ectopic hoxa2 expression (200 pg) results in krox20 expression in the eyes of wild-type embryos (arrow in I), and this effect is also suppressed in lzr/pbx4-/- embryos. Scale bar, 100 μm in (A–H); 200 μm in (I) and (J). |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 253(2), Cooper, K.L., Leisenring, W.M., and Moens, C.B., Autonomous and nonautonomous functions for Hox/Pbx in branchiomotor neuron development, 200-213, Copyright (2003) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.