Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-070918-7
- Publication
- Pujic et al., 2006 - Reverse genetic analysis of neurogenesis in the zebrafish retina
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
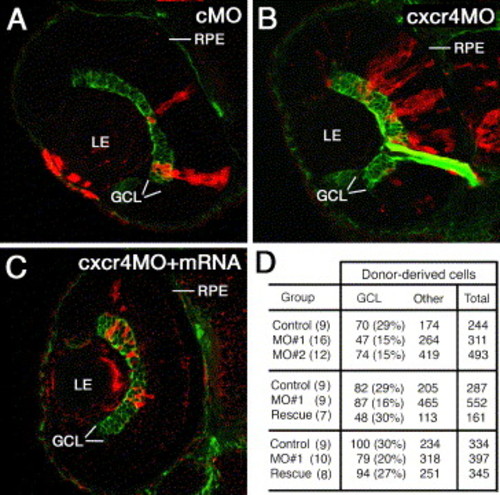
Mosaic analysis of cxcr4b knockdown phenotype. Blastomeres were transplanted into untreated host embryos from sibling donor embryos that were injected with a control MO (A) an anti-cxcr4b MO (B) or a mixture of anti-cxcr4b MO and crcr4b mRNA. The resulting mosaic retinae contain a mix of morpholino-treated donor-derived cells (red) and untreated host cells. The ganglion cell layer (GCL, green) is visualized with the Zn8 antibody. (D) The frequency of GCL cells in clones derived from donor animals treated with a control MO, anti-cxcr4b translation blocking MO (MO#1), anti-cxcr4b splice-site blocking MO (MO#2), or anti MO#1 and cxcr4b mRNA (Rescue). Each row of panel D table shows a separate experiment. In all experiments, morpholino injection resulted in a statistically significant loss of ganglion cells. mRNA treatment restores the wild-type frequency of ganglion cells. The numbers of retinae examined are provided in brackets. GCL, ganglion cell layer; LE, lens; RPE, retinal pigmented epithelium. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 293(2), Pujic, Z., Omori, Y., Tsujikawa, M., Thisse, B., Thisse, C., and Malicki, J., Reverse genetic analysis of neurogenesis in the zebrafish retina, 330-347, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.