FIGURE
Fig. 7
Fig. 7
|
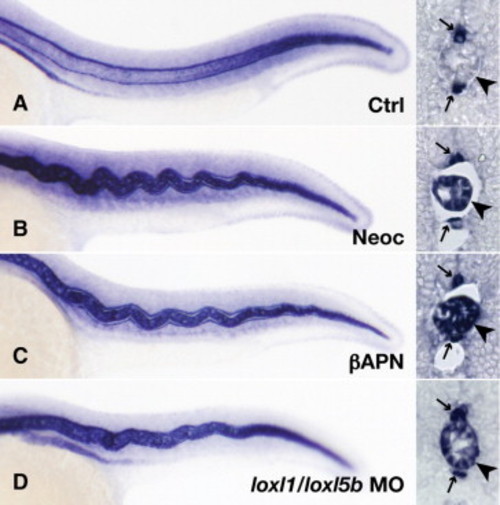
Expression of col2a1 mRNA by notochord vacuolar cells persists late following lysyl oxidase inhibition. Wild-type embryos were injected with 7.4 ng control morpholino (A), incubated in 10 μM neocuproine (B), incubated in 10 mM β-aminopropionitrile supplemented with 10 μM CuCl2 (C), or injected with 3.7 ng each of loxl1 and loxl5b morpholino (D). In situ hybridization was carried out at 24 hpf, and frozen sections confirmed persistent col2a1 expression following lysyl oxidase inhibition (B–D, arrowhead), as well as floorplate and hypochord staining (A–D, arrows). |
Expression Data
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Conditions: | |
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Prim-5 |
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Prim-5 |
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 307(2), Gansner, J.M., Mendelsohn, B.A., Hultman, K.A., Johnson, S.L., and Gitlin, J.D., Essential role of lysyl oxidases in notochord development, 202-213, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.