FIGURE
Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-070206-5
- Publication
- Zecchin et al., 2007 - Distinct delta and jagged genes control sequential segregation of pancreatic cell types from precursor pools in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
Fig. 2
|
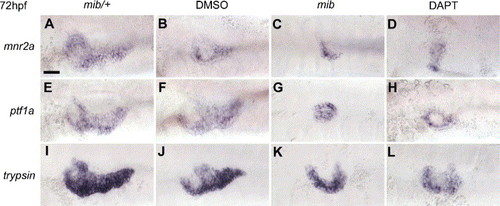
Block of Notch signalling decreases the number of exocrine cells in the pancreas. In situ hybridizations showing reduction of mnr2a (A–D), ptf1a (E–H) and trypsin (I–L) expression in mib mutants (C, G, K) and DAPT-treated embryos (D, H, L). The pancreatic area is depicted. Embryos in panels A, E, I and B, F, J should be compared with embryos in panels C, G, K and D, H, L, respectively. Embryos have been hybridized at 72 hpf and are presented in ventral view with anterior to the left. Scale bar in panel A is 50 μm. |
Expression Data
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Condition: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | Protruding-mouth |
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 301(1), Zecchin, E., Filippi, A., Biemar, F., Tiso, N., Pauls, S., Ellertsdottir, E., Gnugge, L., Bortolussi, M., Driever, W., and Argenton, F., Distinct delta and jagged genes control sequential segregation of pancreatic cell types from precursor pools in zebrafish, 192-204, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.