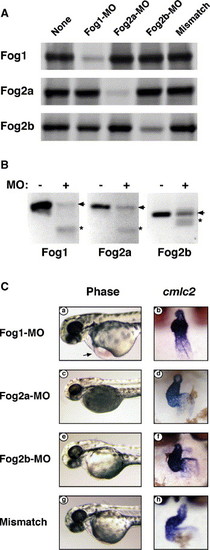
Fog1 is required for cardiac looping. Anti-fog morpholinos inhibit translation or splicing of fog mRNA. In panel A, in vitro transcription and translation of Fog1 (top panel), Fog2a (middle panel), or Fog2b (bottom panel) in the absence (column 1) or presence of gene-specific morpholino (columns 2–4) or mismatch control (column 5). In panel B, RT-PCR of RNA from 48 hpf zebrafish embryos uninjected (-) or injected (+) with morpholinos directed against the exon 4 splice donor site of fog1 (left panel), fog2a (middle panel), or the exon 5 splice donor site of fog2b (right panel) using primers from flanking exons. Arrowheads indicate the correctly spliced product; asterisks indicate aberrantly spliced products. Developmental defects in morpholino injected embryos. In panel C, morpholinos directed against fog1 (a and b), fog2a (c and d), fog2b (e and f) or a mismatch control (g and h) were injected into single-cell zebrafish embryos and embryos photographed 48 h post-fertilization (a, c, e, g). Arrows indicate a pericardial effusion and blood pooling in the atrium. Panels on the right (b, d, f, h) are in situ hybridizations using the cmlc2 probe on 48 hpf morphants.
|

