- Title
-
Transgene expression in zebrafish: a comparison of retroviral-vector and DNA-injection approaches
- Authors
- Linney, E., Hardison, N.L., Lonze, B.E., Lyons, S., and DiNapoli, L.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
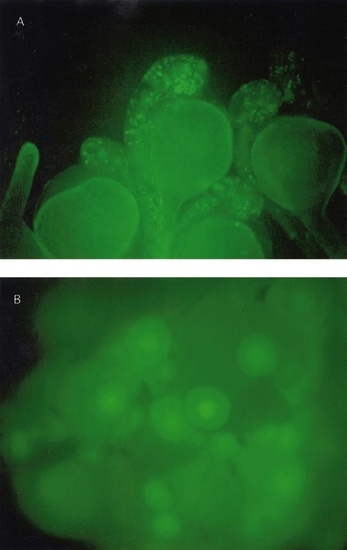
(A) Zebrafish embryos were infected at the 500- to 1000-cell stage with pseudotyped retroviral vector via injection of virions into four separate sites. 24 h after the infection, embryos were examined in the fluorescence microscope for GFP expression. This field is a typical view of the expression obtained. (B) Follicles from an Ef1-α-39-derived adult that was sacrificed to examine the ovaries. Note that the GFP is present in the nucleus (similar observations were made on follicles from a RVEG-19 female). |
|
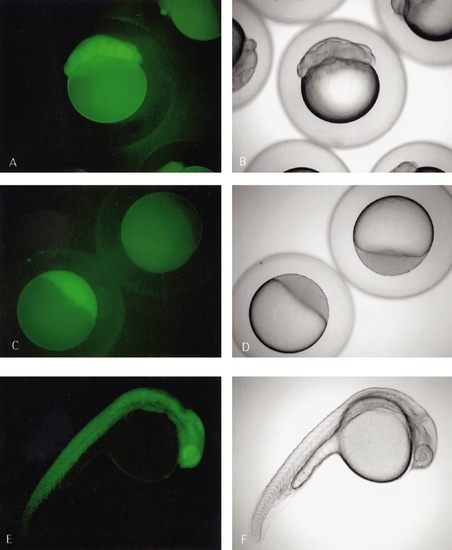
GFP-positive embryos derived from transgenic founder produced via pseudotyped retroviral vector infection. (A and B) 16-cell embryos derived from transgenic female parent—note the GFP even though the zygotic genome has not turned on. (C and D) GFP from a dome-stage embryo—the transgenic embryo in the lower left was derived from a transgenic female parent while the transgenic embryo in the upper right was derived from a transgenic male parent. The fluorescence in the lower left embryo is derived from the oocyte. Even though the zygotic genome is beginning to turn on at this time, we routinely do not detect embryonic GFP until 5–7 h after fertilization. (E and F) 24-h embryo derived from transgenic female parent. |
|
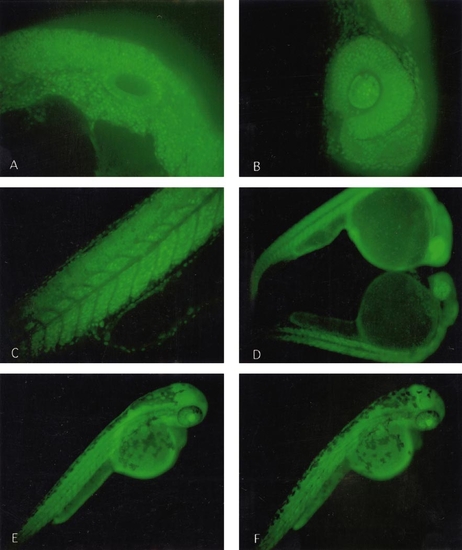
(A, B, and C) Low-power Nipkow disk confocal sections of the embryo illustrated in Fig. 3. These images are of a retroviral vector-produced transgenic embryo. (D, E, and F) Transgenic embryos derived from DNA microinjection. (A) is a section through otic vesicle, (B) is a section through the eye, and (C) is a sagittal section through the tail. Note the nuclear localization of the GFP signal. (D) is a comparison of embryos of the Ef1 α-39 line at 24 h. The upper embryo is derived from a female transgenic parent and the lower embryo is derived from a male transgenic parent. Note that even at 24 h there is a noticeable increase in the GFP signal of the embryo from the female parent. (E) is a 48-h embryo from a female parent and (F) is a 48-h embryo from a male parent. The difference is GFP signal diminishes by this developmental time. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 213(1), Linney, E., Hardison, N.L., Lonze, B.E., Lyons, S., and DiNapoli, L., Transgene expression in zebrafish: a comparison of retroviral-vector and DNA-injection approaches, 207-216, Copyright (1999) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.