- Title
-
Effectiveness of add-on acetazolamide in children with drug-resistant CHD2-related epilepsy and in a zebrafish CHD2 model
- Authors
- Melikishvili, G., Striano, P., Shojeinia, E., Gachechiladze, T., Kurua, E., Tabatadze, N., Melikishvili, M., Koniashvili, O., Khachiashvili, G., Epitashvili, N., Rimma, G., Belyaev, O., Tomenko, T., Kharytonov, V., Guliyeva, U., Esguerra, C.V., Crawford, A.D., Dulac, O.
- Source
- Full text @ Epilepsia Open
|
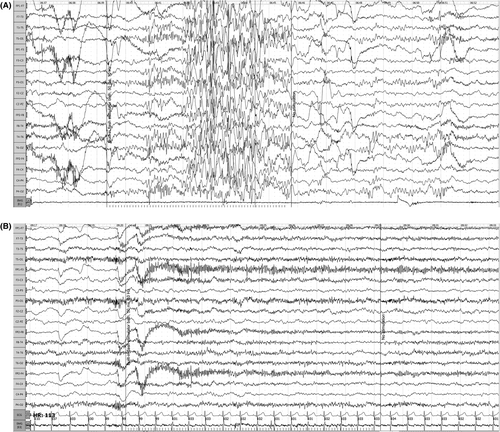
EEG on intermittent photic stimulation (10 Hz), before (A) and on (B) acetazolamide. Amplitude 10 mv/mm, sweep 30 mm/s, low-pass filter −0.5 Hz, high-pass filter −70 Hz. |
|
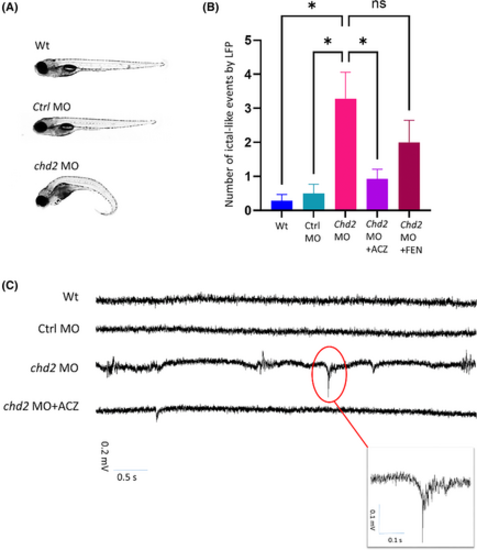
Antisense knockdown of chd2 in zebrafish larvae—morphological and electrophysiological analysis (A) chd2 knockdown and non-injected control zebrafish larvae at 5 dpf. (B-C) Local field potential (LFP) recording revealed epileptiform events in 5-dpf chd2 knockdown larvae; chd2 knockdown larvae exhibited an increase in ictal-like events compared to non-injected control larvae at 5 dpf, non-injected control larvae with a mean of 0.29 ± 0.18 (SEM), chd2 knockdown larvae with a mean of 3.29 ± 0.77, chd2 knockdown treated with 1 mM acetazolamide with a mean of 0.92 ± 0.29, chd2 knockdown treated with 100 μM fenfluramine overnight with a mean of 2.0 ± 0.64 ictal-like events. Statistical analysis by one-way ANOVA showed that treatment with 1 mM acetazolamide significantly reduced ictal-like events (p < 0.05), but that for 100 μM fenfluramine, the result was not significant (p > 0.29), with all groups passing the D'Agostino-Pearson normality test. PHENOTYPE:
|