- Title
-
PAAQ: Paired Alternating AcQuisitions for virtual high frame rate multichannel cardiac fluorescence microscopy
- Authors
- Marelli, F., Ernst, A., Mercader, N., Liebling, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Biol Imaging
|
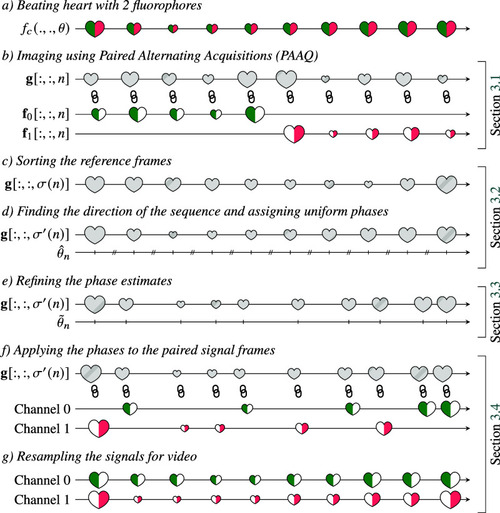
Overview of the proposed PAAQ method for virtual high frame rate cardiac imaging. Chain symbols represent images that we consider as paired because they were acquired in rapid succession. |
|
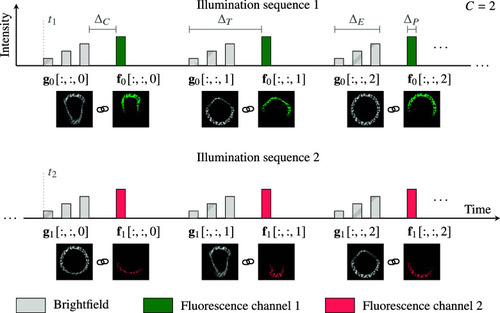
Illumination modulation for PAAQ imaging. Quickly switching between different channels and modalities allows associating fluorescence frames to a common brightfield reference. Chain symbols represent images that we consider as paired because they were acquired in rapid succession. |
|
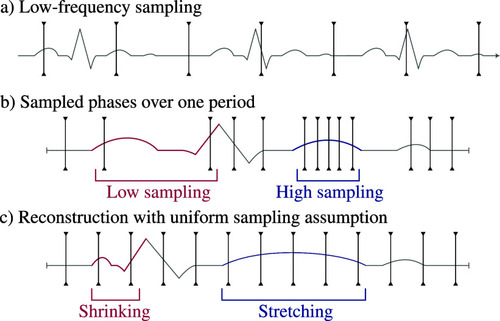
Reconstruction artifacts introduced by the uniform sampling assumption. (a) Fast repeating process sampled with a low frequency. (b) Rearranged over a single period, the sampled points are not uniformly spaced. (c) If assuming a uniform phase sampling, the reconstructed signal is deformed. |
|
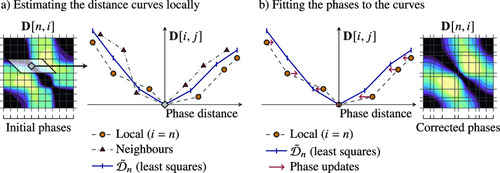
Image-based phase estimation algorithm. (a) We compute a local average distance curve An external file that holds a picture, illustration, etc. Object name is S2633903X23000223_inline84.jpg for each origin position An external file that holds a picture, illustration, etc. Object name is S2633903X23000223_inline85.jpg via least-squares fitting on the measurements An external file that holds a picture, illustration, etc. Object name is S2633903X23000223_inline86.jpg (b) We update the phase estimates by minimizing the distance between local measurements and the computed average distance curves. We iterate over these steps until convergence. The distance matrix An external file that holds a picture, illustration, etc. Object name is S2633903X23000223_inline87.jpg gets smoother as the phase estimates improve. |
|
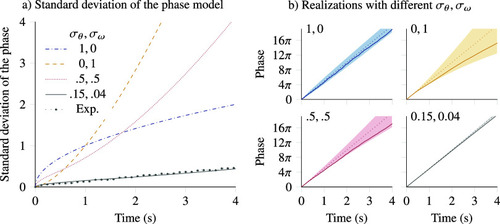
Stochastic phase model for simulating heart rate variability. Our model uses two parameters to represent variability: a phase deviation An external file that holds a picture, illustration, etc. Object name is S2633903X23000223_inline192.jpg and a frequency deviation An external file that holds a picture, illustration, etc. Object name is S2633903X23000223_inline193.jpg . Plots illustrate the model for a simulated 2.5 beats per second signal. (a) Varying the ratio of these contributions changes how fast the phase uncertainty increases, with An external file that holds a picture, illustration, etc. Object name is S2633903X23000223_inline194.jpg generating a rapidly increasing variance. Measurements on experimental data match the simulation model. (b) Realizations of our model in different scenarios show that An external file that holds a picture, illustration, etc. Object name is S2633903X23000223_inline195.jpg generates local noise, while An external file that holds a picture, illustration, etc. Object name is S2633903X23000223_inline196.jpg contributes to bigger smoother variations. The bottom-right panel illustrates values matching experimental measurements. |
|
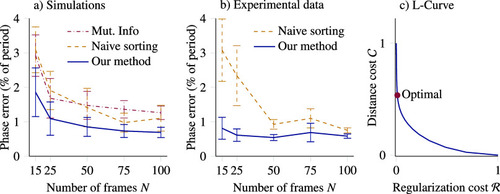
Quantitative results on synthetic and experimental data. Error bars are 68% confidence intervals computed over 10 repetitions. (a) On synthetic data, our method yields a relative precision improvement of 30% over competing methods, independently of the number of frames acquired. (b) On experimental data, our method performs similarly, with a relative precision improvement of up to 50% (for An external file that holds a picture, illustration, etc. Object name is S2633903X23000223_inline211.jpg ). (c) We choose the regularization strength for phase estimation using an L-curve, emphasizing the regularization cost due to strong priors. |
|
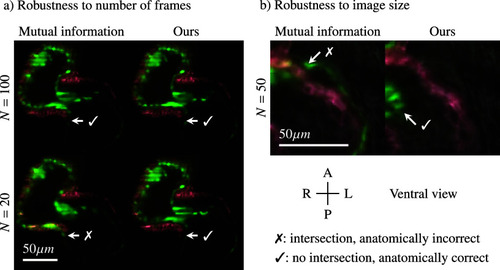
Comparison of the reconstructed videos using our method and a mutual information approach, 4 dpf transgenic Fli1V/Myl7mR zebrafish heartbeat. Cross marks highlight anatomically implausible spots where myocardium (red) intersects with endocardium (green). (a) With high number of frames both methods give similar results, but mutual information gives artifacts with An external file that holds a picture, illustration, etc. Object name is S2633903X23000223_inline233.jpg , while our method is not impacted. (b) When working on small images, mutual information gives incorrect channel synchronization between red and green, while our method generates a plausible solution. See also Supplementary Videos 2–4. |