- Title
-
Deformity or variation? Phenotypic diversity in the zebrafish vertebral column
- Authors
- Martini, A., Sahd, L., Rücklin, M., Huysseune, A., Hall, B.K., Boglione, C., Witten, P.E.
- Source
- Full text @ J. Anat.
|
Schematic of an adult zebrafish highlighting the region of interest (a; modified from Bensimon-Brito, Cardeira, et al., 2012) and SRXTM reconstructions of a normal vertebral body (b and b′). (b) Left side, (b′) right side. Scale bars = 100 μm. PU1 + U1, compound centrum preural 1 and ural 1; PU 2–3, preural 2–3; U2, ural 2; NA, neural arch; NS, neural spine; HA, haemal arch; HS, haemal spine; N and H pre-zyg, neural and haemal pre-zygapophysis; N and H post-zyg, neural and haemal post-zygapophysis. Please note that slight shape alterations not indicated by codes are related to the critical-point-drying procedure of previously whole-mount stained samples. The four-headed arrows indicate sample orientations. |
|
Histogram of the frequency of specimens displaying different phenotypes in the caudal region of the vertebral column. ce fus, complete fusion; ce hemi, hemivertebra; ce red, reduction in length of the centrum; na/ns ins, misplacement of neural arch insertion; na/ns mis, mismatched fusion of neural spines of two different centra; na/ns bif, bifid neural spine; na/ns sup (L/R), supernumerary (L/R) arch/spine; na/ns abs (L/R), absent neural arch/spine; na/ns sv, neural arch/spine shape variation; ha/hs ins, misplacement of haemal arch insertion; ha/hs mis, mismatched fusion of haemal spines of two different centra; ha/hs bif, bifid haemal spine; ha/hs sup (L/R), supernumerary (L/R) haemal arch/spine; ha/hs abs (L/R), absent haemal arch/spine; ha/hs sv, haemal arch/spine shape variation |
|
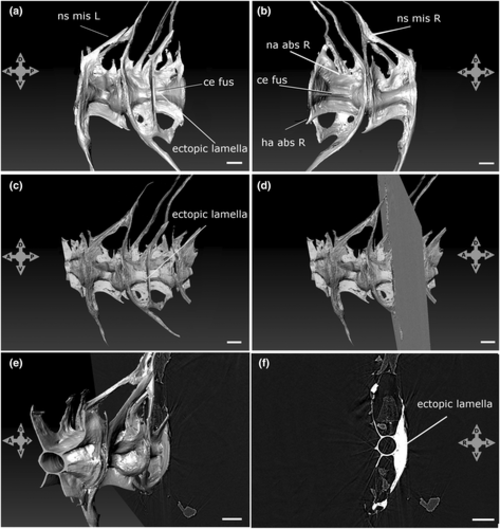
SRXTM reconstruction and volume rendering of a specimen with a fused vertebral body and ectopic lamella. (a and b) SRXTM 3D reconstruction (a) left and (b) right. Refer to Table 1 for variation codes. Volume rendering (c–e) and section (f) of fused vertebral centrum showing the bony lamella. (c) Left view, (d and e) left and oblique view and transverse section plane, (f) transverse section at the level of the bony lamella. Scale bars = 100 μm. The four-headed arrows indicate sample orientations. |
|
Fluorescent (a) and bright-field (b–f) images of whole-mount stained specimens. Refer to Table 1 for the variation codes. Scale bars = 500 μm. The four-headed arrow in panel (a) indicates sample orientation in (a), (b) and (d–f). |
|
Fluorescent (a) and bright-field (b–f) images of whole-mount stained specimens. Refer to Table 1 for the variation codes. Scale bars = 500 μm. The four-headed arrow in panel (a) indicates sample orientation in (a), (b) and (d–f). |
|
SRXTM reconstructions of specimens with hemivertebrae and other arch and spine variations. (a and b) left side, (a′ and b′) right side. Scale bars = 100 μm. Refer to Table 1 for variation codes. Note that slight shape alterations not indicated by codes are related to critical-point-drying procedure of previously whole-mount stained samples. The four-headed arrows indicate sample orientations. |
|
SRXTM reconstructions of specimens with centrum, arch and spine variations. (a–c) left side, (a′–c′) right side. Scale bars = 100 μm. Refer to Table 1 for variation codes. Please note that slight shape alterations not indicated by codes are related to critical-point-drying procedure of previously whole-mount stained samples. The four-headed arrows indicate sample orientation. |
|
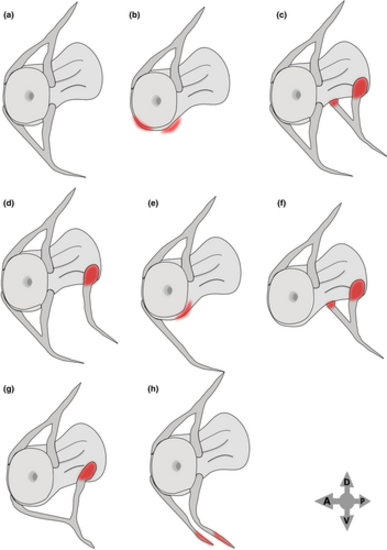
Schematics of different types of neural arch and spine variations. (a) Normal caudal vertebra, (b) missing left and right neural arches and spine, (c) supernumerary left and right neural arches and spine, (d) supernumerary neural arch on one side (left in the scheme), (e) absent neural arch on one side (left in the scheme), (f) posterior shifting of the left and right neural arch insertion, (g) caudal shifting of the neural arch insertion on one side (left in the scheme), (h) unfused neural spine (bifid spine). The four-headed arrow indicates the orientation. |
|
Schematics of different types of haemal arch and spine variations. (a) Normal caudal vertebra, (b) missing left and right haemal arches and spine, (c) supernumerary left and right haemal arches and spine, (d) supernumerary haemal arch on one side (left in the scheme), (e) absent haemal arch on one side (left in the scheme), (f) caudal shifting of the left and right haemal arch insertion, (g) caudal shifting of the haemal arch insertion on one side (left in the scheme), (h) unfused haemal spine (bifid spine). The four-headed arrow indicates the orientation. |
|
Types of vertebrae. (a and a′) aspondylous, (b and b′) monospondylous, (c, c′, c″ and d, d′) diplospondylous with different size and shape (C″ = wedge-shaped vertebrae, hemicentra), (e and e′) Rhizoprionodon's phenotype. Adapted from von Zittel et al. (1911), Šecérov (1911), Schaeffer (1967), Arratia et al. (2001), Peskin et al. (2020) and from Maisey personal communication. |
|
Sketches of the Amia calva caudal skeleton (modified from Schauinsland, 1906). ce fus, centra fusion; ce hemi, hemivertebra; ce red, centra with reduced length; fc, fused cartilage element; lda, large dorsal arch; lva, large ventral arch; nc, notochord; sda, small dorsal arch; sva, small ventral arch. |