- Title
-
Rifaximin potentiates clarithromycin against Mycobacterium abscessus in vitro and in zebrafish
- Authors
- Goh, B.C., Larsson, S., Dam, L.C., Ling, Y.H.S., Chua, W.L.P., Abirami, R., Singh, S., Ong, J.L.E., Teo, J.W.P., Ho, P., Ingham, P.W., Pethe, K., Dedon, P.C.
- Source
- Full text @ JAC Antimicrob Resist
|
Scatter plot of the screening of 2252 compounds. The compounds that resulted in >90% growth inhibition of |
|
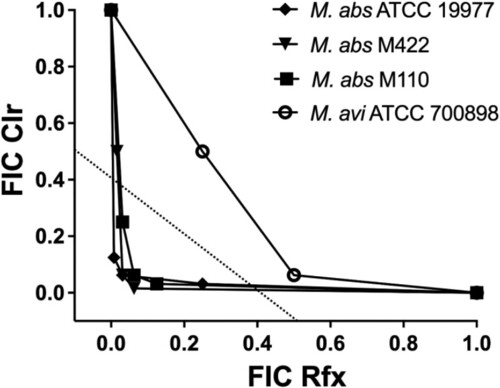
Isobolograms for rifaximin (Rfx) and clarithromycin (Clr) against M. abscessus (M. abs) and M. avium (M. avi) strains. The FIC data points that fall below the dotted line (FICI ≤ 0.5) are defined as synergistic. Note that all three strains of M. abscessus were preinduced whereas the M. avium strain was uninduced. |
|
MBC and MIC determination of the combination of clarithromycin (Clr) and rifaximin (Rfx) on M. abscessus ATCC 19977. The cfu counts were determined for the cells treated with 0.5×, 1×, 2×, 4× and 8 × MIC of clarithromycin in the presence of 1 × MIC of rifaximin, and vice versa. The MBC90 (orange line) was defined as the lowest drug concentration required to induce >90% cell death compared with the starting inoculum (at 0 h timepoint) of the untreated control. The number of residual log10 cfu/mL was determined through plating 10-fold serial dilution and compared with the starting inoculum. Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed Student’s t-test with Welch’s correction; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. The dashed black line indicates the limit of detection. The experiments were carried out in duplicates; error bars represent the SD. |
|
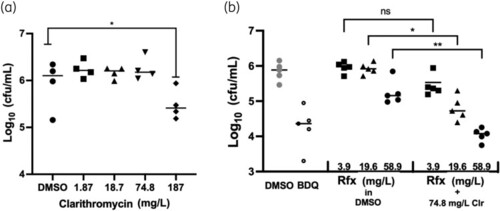
Rifaximin synergizes with clarithromycin to reduce the load of M. abscessus in infected zebrafish larvae. (a) Infected fish treated with various concentrations of clarithromycin. (b) The bacterial burdens of animals treated with rifaximin only were compared with those of animals treated with rifaximin and clarithromycin in combination. Bedaquiline (BDQ; 3 mg/L) was used as a control becuase it has demonstrated efficacy against M. abscessus in zebrafish embryos.24 Note that each dot plotted represents five larvae homogenized together. Fish were infected in the hindbrain ventricle at 48 hours post-fertilization (hpf), and treatment began at 72 hpf. Treatment was maintained for 4 days with daily water changes before the fish were assessed for bacterial burden. Clr, clarithromycin; ns, non-significant; Rfx, rifaximin. |