- Title
-
Zebrafish HERC7c Acts as an Inhibitor of Fish IFN Response
- Authors
- Li, Y.L., Gong, X.Y., Qu, Z.L., Zhao, X., Dan, C., Sun, H.Y., An, L.L., Gui, J.F., Zhang, Y.B.
- Source
- Full text @ Int. J. Mol. Sci.
|
Zebrafish has four herc7 genes that are induced by SVCV infection. (A) Schematic representation of zebrafish herc3 gene locus containing four herc7 homologous genes. (B,C) Four zebrafish herc7 genes were transcriptionally induced in SVCV-infected zebrafish tissues. Zebrafish adults were intraperitoneally injected with SVCV for 48 h, followed by RT-PCR analyses of ifnφ1, ifnφ3, and mxc (B), as well as herc7a-d (C), in different zebrafish tissues. |
|
Zebrafish herc7c is a typical ISG. (A) Amplification of full-length cDNA (left) and fragment (right) of the herc7c gene. (B) Exon–intron structure and transcriptional splicing analysis of the zebrafish herc7c genome. The black box represents the exon. The red dotted box indicates the difference area among the possible spliceosomes. The red arrows mark the locations of the check primers. (C) The 5′ flanking sequence of zebrafish herc7c. Two ISRE motifs and the transcription start site are highlighted in red. Their respective positions are numerically marked in the sequence. (D) Schematic diagram of luciferase reporter plasmids under the control of 5′-flanking sequence of zebrafish herc7c gene and the derived truncates and point mutants. (E,F) Zebrafish HERC7c promoter was activated through the RLR signaling pathway and th eJAK-STAT pathway. EPC cells were co-transfected with 200 ng luciferase reporter plasmid (pGL3-Basic or HERC7cpro-Luc), together with 300 ng of each plasmid annotated in the figure. (G) Intracellular poly(I:C) stimulated-activation of zebrafish HERC7c promoter was blocked by overexpression of dominant negative mutants involved in the RLR pathway and the JAK-STAT pathway. (H) Zebrafish HERC7c promoter was activated by intra-poly(I:C), extra-poly(I:C), and SVCV. EPC cells were transfected with 200 ng HERC7cpro-Luc (left panel), or individually with HERC7cpro-Luc and 2 truncated promoter plasmids [(−888~−249) pro-luc, (−248~−1) pro-luc] (right panel). After 12 h, the cells were transfected again with 1 μg/mL poly(I:C) or directly incubated with 50 μg/mL poly(I:C) or infected with SVCV (final titer at 103 TCID50/mL). (I) ISRE motifs were responsible for zebrafish HERC7c promoter activation by intra-poly(I:C). EPC cells were transfected with HERC7cpro-Luc or with 3 ISRE-mutated luciferase plasmids (200 ng each). (*** p < 0.001). |
|
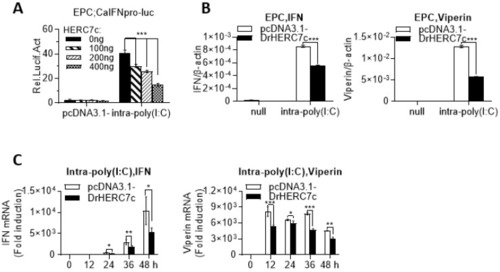
Zebrafish HERC7c suppresses intracellular poly(I:C)-triggered IFN response by luciferase assays. (A) Overexpression of zebrafish HERC7c inhibited fish IFN promoter activation by intracellular poly(I:C). EPC cells were cotransfected with 100 ng CaIFNpro-luc and increasing doses of zebrafish HERC7c for 24 h, followed by transfection with 1 μg /mL poly(I:C). (B,C) Zebrafish HERC7c inhibited mRNA expression of cellular ifn and viperin in EPC cells by intracellular poly(I:C). EPC cells were transfected with 2 μg of zebrafish HERC7c or pcDNA3.1- as control. After 12 h, the cells were transfected again with 1 μg/mL poly(I:C). At 36 h post infection (B) or at different time points (C), cells were sampled for RT-PCR analyses of cellular ifn and mx transcription. Error bars represent SD obtained by measuring each sample in triplicate. (*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05). |
|
Zebrafish HERC7c promotes virus replication in fish cells. (A,B) Overexpression of zebrafish HERC7c promoted viral replication. EPC cells seeded in 24-well plates were transfected for 24 h with 500 ng HERC7c or pcDNA3.1 as control, followed by infection with SVCV at different titers (A) or at 1 × 103 TCID50/mL (B). After 72 h, the cells were stained with crystal violet for detection of CPE (A), or 24 h later, the cells were collected for RT-PCR analyses of SVCV gene transcription. (C–E) SVCV replication was facilitated by overexpression of zebrafish HERC7c. EPC cells seeded in 24-well plates overnight were transfected for 12 h with HERC7c (0.5 µg) or pcDNA3.1(-) as control, followed by infection with SVCV. After 72 h (C), or at different time points (D,E), cells were sampled for RT-PCR detection of cellular ifn and viperin expression (C,D), and SVCV gene expression (E). (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001). |
|
Zebrafish HERC7c suppresses the IFN response by targeting STING, MAVS, and IRF7. EPC cells seeded in 24-well plates were transfected with 100 ng DrIFNφ1pro-luc or DrIFNφ3pro-luc and increasing doses of HERC7c (0 ng, 50 ng, 100 ng, and 400 ng), together with 300 ng of zebrafish STING (A), MAVS or IRF7 (B), and TBK1 or IRF3 (C). After 24 h, the cells were collected for luciferase assays. Error bars represent SD obtained by measuring each sample in triplicate. (*** p < 0.001, ns: no significant). |
|
Zebrafish HERC7c attenuates STING, MAVS, and IRF7 protein levels to downregulate the IFN response.(A,B) Zebrafish HERC7c attenuated STING-directed ifn gene transcription but not sting gene transcription. EPC cells seeded in 3.5 cm2 dishes were cotransfected with zebrafish STING-HA and zebrafish HERC7c-Flag (1 μg each) for different time points, followed by RT-PCR analysis of cellular ifn and viperin (A) and the transfected herc7c and sting (B). Error bars represent SD obtained by measuring each sample in triplicate. (C) Zebrafish HERC7c attenuated zebrafish STING protein level. EPC cells seeded in 3.5 cm2 dishes were cotransfected with zebrafish HERC7c-Flag and zebrafish STING-HA (1 μg each) for different time points, followed by Western blotting analyses of STING protein. (D–F) Zebrafish HERC7c attenuated IRF7- or MAVS-directed ifn gene transcription. EPC cells were cotransfected as in (A,B) by replacing zebrafish STING with zebrafish IRF7 or MAVS, followed by RT-PCR analyses (D,E) or Western blotting (F). |
|
Zebrafish HERC7c-mediated degradation of STING, MAVS, and IRF7 was blocked by MG132 but not by chloroquine. EPC cells seeded in a 12-well plate were cotransfected with DrHERC7c-Flag and DrSTING-HA (A), DrMAVS-HA (B), or DrIRF7-HA (C), respectively. After 24 h, the cells were treated with MG132 (final concentration of 10 mM) and chloroquine (final concentration of 25 mM) for another 6 h, followed by Western blotting. |
|
Zebrafish HERC7c is an E3 ligase for the conjugation of ubiquitin rather than ISG15. (A) Schematic diagram of zebrafish HERC7c protein and crucian carp HERC7 protein. (B) Polyubiquitination of zebrafish HERC7c. HEK293T cells plated in 10 cm2 dishes overnight were transfected with 5 μg zebrafish HERC7c-HA together with or without 4 μg His-Ub. After 30 h, cells lysates were incubated with Ni2+-NTA resin, followed by Western blotting. (C) ISGylation of crucian carp HERC7 but not of zebrafish HERC7c. HEK293T cells plated in 10 cm2 dishes were transfected with zebrafish HERC7c-HA or crucian carp HERC7-HA (5 μg each), together with or without 5 μg Flag-ISG15. After 30 h, the cells were collected for Western blotting. |
|
Phylogenetic evolutionary analysis of HERC7 subfamily containing zebrafish HERC7c. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using the neighbor-joining methods, and the bootstrap sampling was performed with 1000 replicates. The GenBank Accession Numbers of sequences are shown in brackets. |