- Title
-
Immunogenetic losses co-occurred with seahorse male pregnancy and mutation in tlx1 accompanied functional asplenia
- Authors
- Liu, Y., Qu, M., Jiang, H., Schneider, R., Qin, G., Luo, W., Yu, H., Zhang, B., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, Z., Wu, Y., Zhang, Y., Yin, J., Zhang, S., Venkatesh, B., Roth, O., Meyer, A., Lin, Q.
- Source
- Full text @ Nat. Commun.
|
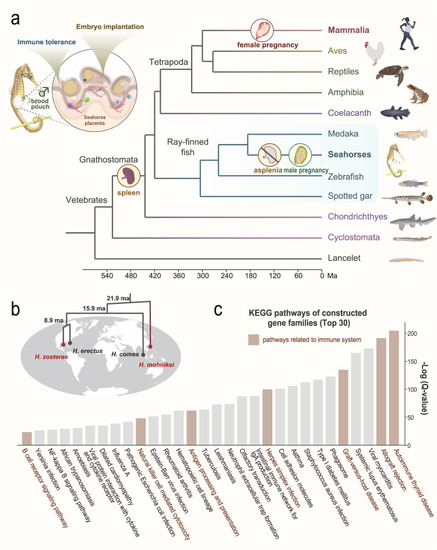
Unique features of immunity and reproduction in seahorses. |
|
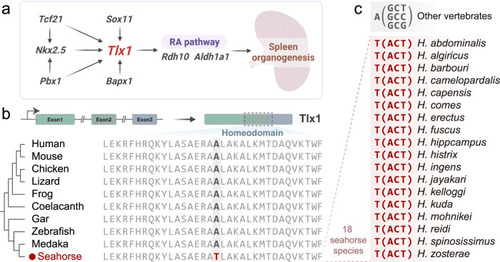
Seahorse-specific mutation of the tlx1 gene. |
|
Missense mutation of tlx1 controls asplenia phenotype in zebrafish. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
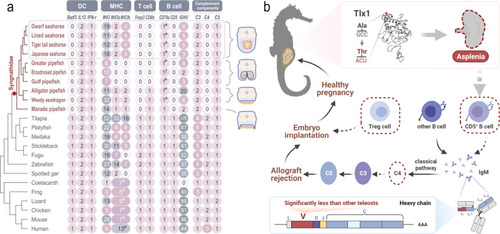
Immunogenomic basis of asplenia and male pregnancy in seahorses. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |