- Title
-
Organophosphate Insecticide Toxicity in Neural Development, Cognition, Behaviour and Degeneration: Insights from Zebrafish
- Authors
- Neylon, J., Fuller, J.N., van der Poel, C., Church, J.E., Dworkin, S.
- Source
- Full text @ J Dev Biol
|
The physiological action of acetylcholine (ACh; purple triangles) at the neuronal cell synapse, the breakdown of ACh through acetylcholinesterase (AChE; orange diamonds), and the phosphorylation of AChE through organophosphate insecticide (OP; red hexagons) exposure. |
|
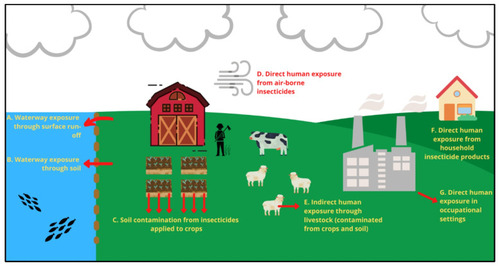
The primary direct and indirect routes of organophosphate (OP) exposure on target and non-target organisms in agricultural, household and aquatic environments. |
|
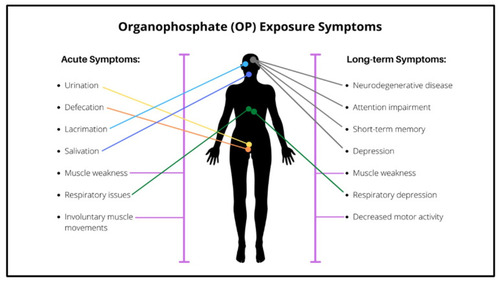
The major consequences of OP exposure in humans. |
|
The symptoms of organophosphate (OP) exposure at progressive time points; acute cholinergic syndrome (ACS) occurs within minutes of OP exposure, symptoms of intermediate syndrome (IMS) display at 1–4 days after OP exposure, and symptoms of organophosphate-induced delayed neuropathy (OPIDN) occur ~2–3 weeks after OP exposure. |