- Title
-
Embryonic Nicotine Exposure Disrupts Adult Social Behavior and Craniofacial Development in Zebrafish
- Authors
- Borrego-Soto, G., Eberhart, J.K.
- Source
- Full text @ Toxics
|
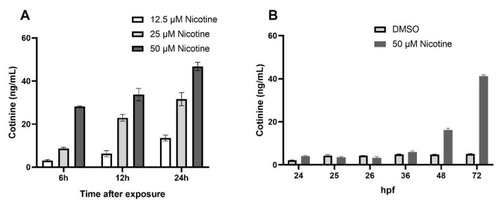
Cotinine levels in zebrafish embryo increases with the time of exposure. ( |
|
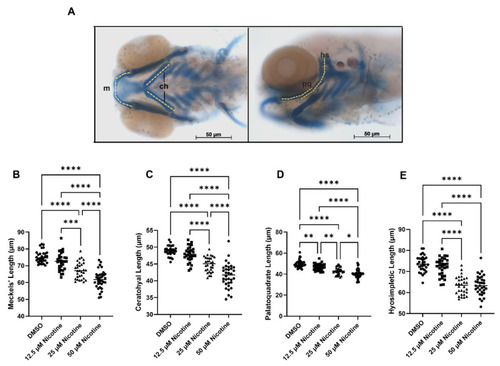
Embryonic nicotine exposure disrupts craniofacial development. Representative whole mount, neurocranial, and viscerocranial flat mount preparation after nicotine exposure from 6 hpf to 4 dpf. Decreases in the size of the craniofacial skeleton were observed as nicotine concentration increased. All images were captured at 10× magnification. Scale bar 50 µm. |
|
Embryonic nicotine exposure effects viscerocranial cartilages length. ( |
|
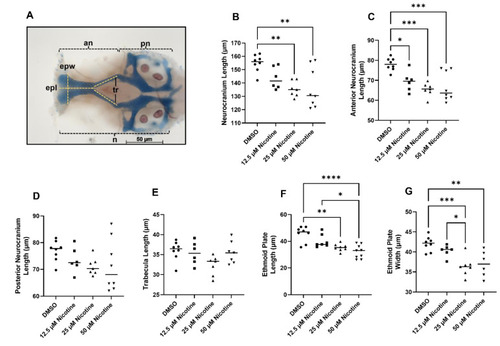
Embryonic nicotine exposure reduces cartilage in the neurocranium. ( |
|
Embryonic nicotine exposure reduces the shoaling response in adult zebrafish. Average distance between the experimental fish and the live shoal, plotted by minute of the 20-min behavioral session. Mean ± SEM is shown. A t-test was used to calculate significance between two groups. ( |
|
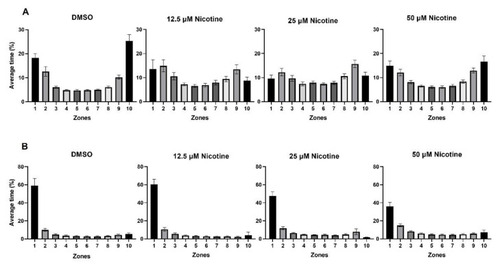
Embryonic nicotine exposure reduces the time fish spend near a live shoal. ( |
|
Embryonic exposure to 50 µM nicotine significantly reduces the time spent near a live shoal. Bars represent the average percentage of time spent in the zone closest to the live shoal while the live shoal was visible. * = |
|
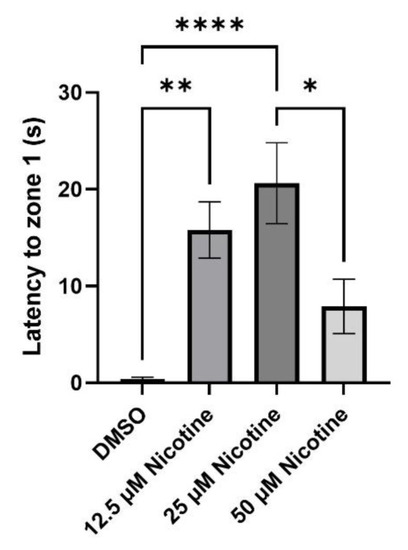
Embryonic nicotine exposure alters the immediate response to a social stimulus in adult zebrafish. Bars represent the time fish take to reach zone 1 once the shoal is visible. While 50 µM nicotine exposure does not change the time to reach 1 one, both the 12.5 µM and 25 µM groups were slower to reach zone 1. * = |
|
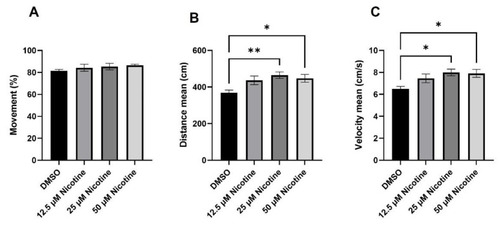
Embryonic nicotine exposure increases locomotion activity in zebrafish adults. Bars represent ( |