- Title
-
The effect of fish density and tank size on the behavior of adult zebrafish: A systematic analysis
- Authors
- Shishis, S., Tsang, B., Gerlai, R.
- Source
- Full text @ Front. Behav. Neurosci.
|
Immobility is affected by prior fish density and home tank size. Panel |
|
Speed is affected by prior fish density and home tank size. Panel |
|
Intra-individual variance of speed is affected by prior fish density and home tank size. Panel |
|
Absolute turn angle is affected by prior fish density and home tank size. Panel |
|
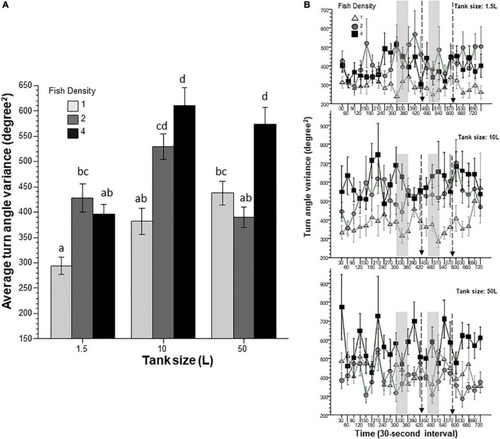
Intra-individual variance of absolute turn angle is affected by prior fish density and home tank size. Panel |
|
Duration of high mobility is affected by prior fish density and home tank size. Panel |
|
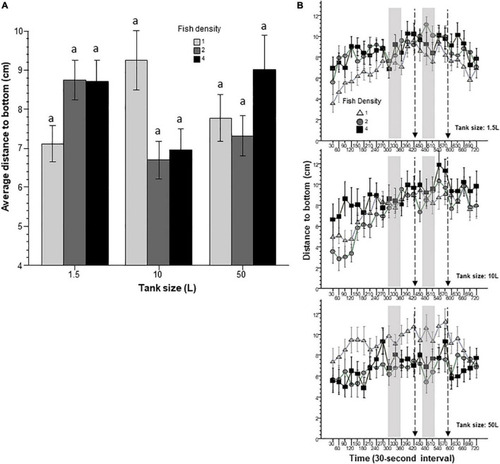
Distance to bottom is affected by prior housing conditions. Panel |
|
Intra-individual temporal variance of distance to bottom appears to be affected by prior housing conditions. Panel |
|
Distance to stimulus screen is affected by prior fish density. Panel |