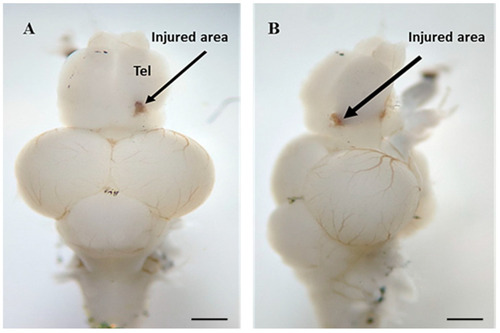
- Title
-
Saffron Extract Attenuates Anxiogenic Effect and Improves Cognitive Behavior in an Adult Zebrafish Model of Traumatic Brain Injury
- Authors
- Chaoul, V., Awad, M., Harb, F., Najjar, F., Hamade, A., Nabout, R., Soueid, J.
- Source
- Full text @ Int. J. Mol. Sci.
|
Effect of saffron on induced-TBI zebrafish behavior in novel tank diving test on days 3, 10 and 21 post-lesion. ( |
|
Effect of saffron on induced-TBI zebrafish behavior in the light/dark test on days 3, 10 and 21 post-lesion. Time spent in the light area (s) in CTL-saffron ( |
|
Effect of saffron on induced-TBI zebrafish behavior in the predator test on days 3, 10 and 21 post-lesion. Time spent near the predator comparisons between CTL-saffron ( |
|
Active avoidance test on zebrafish 12 days post-injury to evaluate the effect of saffron on learning, short-term memory (STM) and long-term memory (LTM). ( |
|
( |