- Title
-
The neuromeric/prosomeric model in teleost fish neurobiology
- Authors
- Wullimann, M.F.
- Source
- Full text @ Brain Behav. Evol.
|
Brain schematics in lateral view for amniotes (a, d), teleosts (b, e) and amphibians (c, f) point out neuromeric divisions. Left side panels [a–c; adapted from Wullimann, 2020] emphasize forebrain with pretectal (P1) prosomere in dark gray, (dorsal) thalamic (P2) prosomere in green and ventral thalamic/prethalamic (P3) in blue. Note that for reasons given in the text, an early version of the amniote prosomeric model [Puelles and Rubenstein, 1993] is given in (a, d). In contrast, the zebrafish model follows in general that proposed by Wullimann and Puelles [1999]. Positions of early migrated teleostean forebrain areas M1 through M4 are highlighted (orange structures in B). In midbrain and hindbrain (a–c), primary neuromeric locations of motor nuclei (red) are shown [after Gilland and Baker, 2005, zebrafish efferent octavolateralis and facial motor neurons after Beiriger et al., 2021]. Right side panels [d–f; adapted from Vernier and Wullimann, 2009] emphasize basal plate portions of prosomeres (bPs in dark gray) and dopamine systems in midbrain and forebrain (pink structures) interpreted within the neuromeric model. Mouse A8-A15 dopamine cell groups correspond to the nomenclature of Smeets and González [2000] and Björklund and Dunnett [2007]. The Arabic numbers of zebrafish dopamine cell groups are taken from Rink and Wullimann [2002]. Xenopus dopamine nuclei are according to González et al. [1994a, b], González and Smeets [1994], Smeets and González [2000], and Xavier et al. [2017]. The inset in (d) shows Ngn2 expression in the mouse diencephalon at this sagittal section level (modified from Osório et al. [2010]; see text). In the hindbrain (d, e) secondary (tangentially migrated) positions of various motor nuclei (red-rimmed) are shown [after Gilland and Baker, 2005; zebrafish efferent octavolateralis and facial motor neurons after Beiriger et al., 2021]. Prosomeric and rhombomeric boundaries are indicated by dashed lines. g Postembryonic zebrafish brain proliferation zones visualized either with PCNA [Wullimann and Puelles, 1999; Wullimann and Knipp, 2000] or BrdU [Mueller and Wullimann, 2002a] support prosomeric model [Puelles and Rubenstein, 1993]. Modified from Mueller and Wullimann [2016]. Alar plate (dorsal) and basal plate (ventral) are separated by a chain line along the anteroposterior axes (note flexures deviating from general body axis; see text). h Schema shows larval brain zebrafish brain schema in lateral view with indication of general body axes on top and in red the anteroposterior and dorsoventral (alar-basal) neuraxes that respect the brain curvature [modified from Herget et al., 2014]. Additionally, intrahypothalamic neuraxes are indicated, and tuberal (gray) and mammillary (light blue) basal hypothalamic parts are highlighted (see text for details). i Larval zebrafish basal hypothalamus with various landmark-providing markers [after Wang et al. [2001]; Rink and Guo [2004]; Forlano and Cone [2007], general basal hypothalamic gene expression (see text for citations) and specific tuberal (TubH) and mammillary hypothalamic (MamH) gene expression after Schredelseker and Driever [2020]. a, anterior; ac, anterior commissure; AEP, anterior entopeduncular area (mouse); Agrp, Agouti-related protein; AH, anterior hypothalamus (mouse); bP1-3, basal parts of prosomeres 1–3; Ce, cerebellum; CeP, cerebellar plate; Crhbp, corticotropin-releasing hormone binding protein; d(a), dorsal(alar); Dop, dopamine; DT, dorsal thalamus; E, epiphysis; EGL, external granular layer; EmT, eminentia thalami; H, hypothalamus; Ha, habenula; Hc, Hi, Hr, caudal, intermediate, rostral periventricular hypothalamic zone; HC, hypothalamic cell cord (mouse); Hist, histamine; InCo, inferior colliculus; M1, early migrated pretectal aera; M2, early migrated posterior tubercular area (preglomerular complex); M3, early migrated area of eminentia thalami; M4, early migrated telencephalic area; MA, mammillary hypothalamus (mouse); MamH, mammillary hypothalamus (zebrafish); md, mediodorsal tectal proliferation; MO, medulla oblongata; MSH, α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone; mv, medioventral tectal proliferation; N, area of the nucleus of the medial longitudinal fascicle; OB, olfactory bulb; oc, optic chiasm; p, posterior; P, pallium; P1-P3, prosomeres 1–3; PEP, posterior entopeduncular area (mouse); Po, preoptic region; POA, anterior preoptic area (mouse); poc, postoptic commissure; POP, posterior preoptic area (mouse); Pr, pretectum; PTd, dorsal posterior tuberculum; PTv, ventral posterior tuberculum; PTM, posterior tectal membrane; RCH, retrochiasmatic hypothalamus (mouse); RCT, rostral cerebellar thickening (valvula); Rho-AP, alar plate proliferation of rhombencephalon; Rho-BP, basal plate proliferation of rhombencephalon; RL, rhombic lip; S, subpallium; SC, spinal cord; Sd, dorsal division of subpallium; SePr, secondary prosencephalon; SH, suprachiasmatic area (mouse); SPV, supraopto-paraventricular area; SuCo, superior colliculus; Sv, ventral division of subpallium; T, midbrain tegmentum; TeO, tectum opticum; TeVe, tectal ventricle; TS, torus semicircularis; TU, tuberal hypothalamus (mouse); TubH, tuberal hypothalamus (zebrafish); v(b), ventral(basal); Va, valvula cerebelli; VCP, ventral cerebellar proliferative layer; Ve, forebrain ventricle; VT, ventral thalamus (prethalamus); VTA/SN, ventral tegmental area/substantia nigra, x location of ventricular proliferation zone of EmT; ZLI, zona limitans intrathalamica. 1–8 rhombomeres 1 through 8, additionally in panel e: 1–7 designate larval zebrafish dopaminergic cells groups (see text for details), III, IV,V (Va/Vp), VI (VIa/VIp), VII, VIII, IX, X, XII ocolumotor, trochlear, trigeminal (anterior/posterior trigeminal), abducens (anterior/posterior abducens), facial, octavolateralis efferent, glossopharyngeal, vagal, hypoglossal motor nuclei, 5-HT 5-hydroxytryptamine. |
|
Zebrafish adult forebrain neuroanatomy shown in transverse Bodian silver/cresyl stained sections [panels modified from Wullimann et al., 1996, see there for full account]. a Precommissural telencephalon. b Commissural telencephalon level. d Rostral diencephalon. e Caudal diencephalon. These four levels show peripherally migrated forebrain cell areas (highlighted with red letters), such as subpallial (Vc, Vl), entopeduncular (ENd, ENv), pretectal (CPN, PSp, PSm, DAO) and preglomerular nuclei (PGl, PGm) (see text). c Shows preoptic region in between (b, d). f Slightly more caudal level than (e) with intermediate nucleus of Hd (see text). g Most caudal diencephalic section with posterior and lateral recess at the same transverse level of caudal hypothalamus (Hc; see text). h Lateral view of adult zebrafish brain with transverse section levels indicated. i Shows drawing of parasagittal section through zebrafish preoptic region (black) [modified from Herget et al., 2014]. Note that the suprachiasmatic nucleus (shown in c) is lateral to the section level. Red line is alar-basal plate boundary. Scale bars, 200 µm. A, anterior thalamic nucleus; ac, anterior commissure; acd, acv, dorsal, ventral anterior commissure; APN, accessory pretectal nucleus [of Wullimann and Meyer [1990]; ATN, anterior tuberal nucleus; CC, cerebellar crest; CCe, corpus cerebelli; CM, corpus mamillare; CP, central posterior thalamic nucleus; CPN, central pretectal nucleus; DAO, dorsal accessory optic nucleus; Dc Dd, Dl, Dm, Dp, central, dorsal, lateral, medial, posterior zone of dorsal telencephalic area; DiL, diffuse nucleus of the inferior lobe; DiV, diencephalic ventricle; dot, dorsomedial optic tract; DP, dorsal posterior thalamic nucleus; DT, dorsal thalamus; EG, eminentia granularis; ENd, ENv, dorsal, ventral entopeduncular nucleus; fr, fasciculus retroflexus; H, (basal) hypothalamus; Ha, habenula; Had, dorsal habenular nucleus; Hav, ventral habenular nucleus; hc, horizontal commissure; Hc, Hd, Hv, caudal, dorsal, ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus; IN, intermediate nucleus of Hd; lfb, lateral forebrain bundle; LH, lateral hypothalamic nucleus; LI, lobus inferior; LL, lateral line nerves; lot, lateral olfactory tract; LR, lateral recess of diencephalic ventricle; mfb, medial forebrain bundle; MO, medulla oblongata; mot, medial olfactory tract; OB, olfactory bulb; oc, optic chiasma; ot, optic tract; pc, posterior commissure; PG, preglomerular complex; PGI, lateral preglomerular nucleus; PGm, medial preglomerular nucleus; Pit, pituitary; PM, magnocellular preoptic nucleus; PMg, gigantocellular part of PM; poc, postoptic commissure; PPa, anterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus; PPd, dorsal periventricular pretectal nucleus; PPp, posterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus; PPv, ventral periventricular pretectal nucleus; PSm, magnocellular superficial pretectal nucleus; PSp, parvocellular superficial pretectal nucleus; PTN, posterior tuberal nucleus; PVO, paraventricular organ; SC, suprachiasmatic nucleus (spinal cord in H); SD, saccus dorsalis; SY, sulcus ypsiloniformis; tc, tectal commissure; Tel, telencephalon; TeO, tectum opticum; TeV, tectal ventricle; TH, tuberal hypothalamus; TL, torus longitudinalis; TLa, torus lateralis; TP, posterior tuberculum; TPp, periventricular nucleus of TP; tpm, tractus pretectomamillaris; Vc, Vd, Vl, Vs, Vv, central, dorsal, lateral, supracommissural, ventral nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; VL, ventrolateral thalamic nucleus; VLo, vagal lobe; VM, ventromedial thalamic nucleus; vot, ventrolateral optic tract; VT, ventral thalamus (prethalamus); I, olfactory nerve; II, optic nerve; IV, trochlear nerve; V, trigeminal nerve; VII, facial nerve; X, vagal nerve. |
|
a–d Zebrafish larval forebrain neuroanatomy shown in transverse Hu-protein stained sections. a Commissural telencephalon with early migrated telencephalic area M4. b Postcommissural telencephalon with early migrated area of eminentia thalami M3. c Rostral diencephalon with early migrated posterior tubercular area M2 (preglomerular complex) and early migrated pretectal area M1. d Caudal diencephalon with early migrated posterior tubercular area M2 (preglomerular complex). e Summary of larval diencephalic zebrafish gene expression patterns (see text for details). f Posteroventral hypothalamic level shows lateral and posterior ventricular recess. Panels (a–f) modified from Mueller and Wullimann [2016]; see there for full account. a1–b1 Corresponding sections with diagnostic regulatory gene markers to identify larval zebrafish migrated areas M4 and M3 [panels modified from Mueller et al., 2008]. ac, anterior commissure; ALLG, anterior lateral line ganglion; bHLH, basic helix-loop-helix; DT, dorsal thalamus; E, epiphysis; EmT, eminentia thalami; Ha, habenula; Hc, Hi, Hr, caudal, intermediate, rostral periventricular hypothalamic zone; lfb, lateral forebrain bundle; LR, lateral ventricular recess of periventricular hypothalamus; M1, early migrated pretectal aera; M2, early migrated posterior tubercular area (preglomerular complex); M3, early migrated area of eminentia thalami; M4, early migrated telencephalic area; mlf, medial longitudinal fascicle; MO, medulla oblongata; oc, optic chiasma; P, pallium; pc, posterior commissure; Po, preoptic area; poc, postoptic commissure; Pr, pretectum; PR, posterior ventricular recess of periventricular hypothalamus; PT, posterior tuberculum; Sdp, posterior subdivision of dorsal part of subpallium (subpallial amygdala homolog); SPV, supraopto-paraventricular region; T, midbrain tegmentum; TeO, tectum opticum; TG, trigeminal ganglion; TS, torus semicircularis; ZLI, zona limitans intrathalamica. For gene names see text. |
|
Development of larval zebrafish subpallium. Transverse sections show precommissural (a) and commissural (b) telencephalon, as well as medial amygdala and eminentia thalami in early mouse and zebrafish postcommissural telencephalon (c) with critical gene expression [modified from Gerlach and Wullimann, 2021; see there for more references on mouse and zebrafish gene expression]. Solid arrows designate radial migrations, dotted arrows designate tangential migrations. ac, anterior commissure; CGE, caudal ganglionic eminence; Dl, lateral zone of dorsal telencephalic area; Dm, medial zone of dorsal telencephalic area; DP, dorsal pallium (isocortex); DT, dorsal thalamus; ENv, ventral entopeduncular nucleus; EmT, eminentia thalami; Hy, hypothalamus; lfb, lateral forebrain bundle; LVe, lateral (telencephalic) ventricle; M3, early larval migration zone of eminentia thalami (= ENv); M4, early larval telencephalic migration zone (subpallial); MeA, medial amygdala; MP, medial pallium; Po, preoptic area (zebrafish); POA, anterior preoptic area (mouse); Pr, pretectum; Sd, larval dorsal part of subpallium; Sdd, dorsal subdivision of Sd (striatum homomog); Sdv, ventral subdivision of Sd (pallidum homolog); Sdp, posterior subdivision of Sd (subpallial amygdala homolog); SPV, supraopto-paraventricular region; Sv, larval ventral part of subpallium (septum homolog); TelCh, tela choroidea; Vi, intermediate nucleus of ventral telencephalon (medial amygdala homolog); VP, ventral pallium (pallial amygdala); VT, ventral thalamus (prethalamus). For gene names see text. |
|
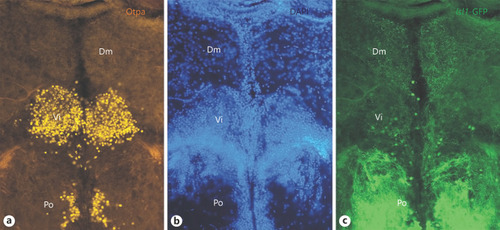
Transverse sections through the zebrafish most caudal amygdalar formation, shows the intermediate nucleus of ventral telencephalon (Vi), the homolog of the medial amygdala. a Otpa, DAPI (b) and Islet1-GFP (c). Note fine Islet1-positive terminals in medial zone of dorsal telencephalon (Dm). See text for details. Abbreviations: Dm, medial zone of dorsal telencephalon, Po, preoptic region. |