- Title
-
alms1 mutant zebrafish do not show hair cell phenotypes seen in other cilia mutants
- Authors
- Parkinson, L., Stawicki, T.M.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
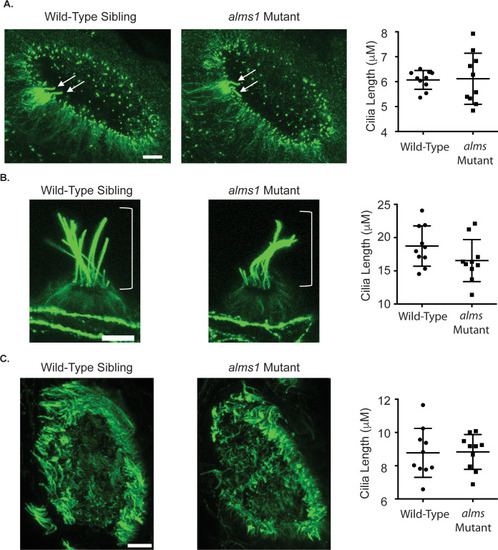
(A) Representative images of the otic vesicle of a 24 hpf wild-type (left) and |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
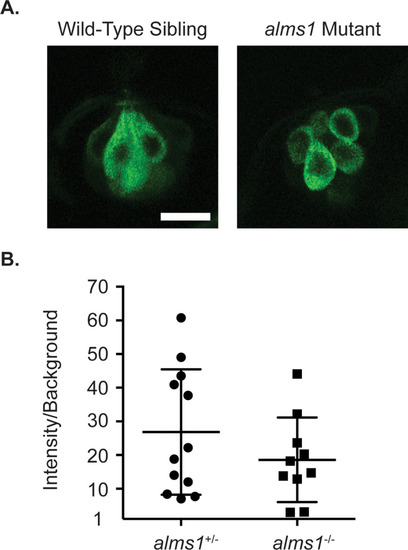
(A) Representative images of neuromasts from wild-type siblings (left) and |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
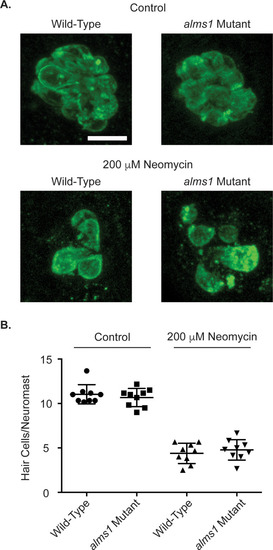
(A) Representative images of neuromasts from control (top) and neomycin treated (bottom) fish from wild-type (left) and PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|