- Title
-
Developmental Accumulation of Gene Body and Transposon Non-CpG Methylation in the Zebrafish Brain
- Authors
- Ross, S.E., Hesselson, D., Bogdanovic, O.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Cell Dev Biol
|
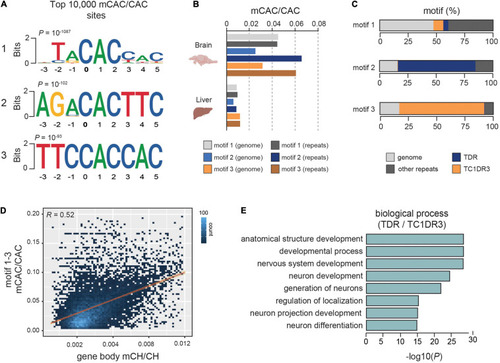
mCH is enriched at defined CAC-containing motifs in zebrafish brains. |
|
mCH is present at long genes with low expression levels. |
|
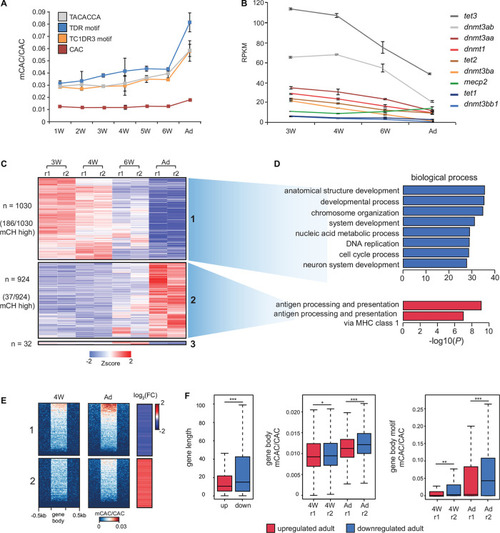
mCH accumulates in the developing nervous system. |
|
Dnmt3a enzymes are required for methylation of CAC trinucleotides in the zebrafish brain. |