FIGURE SUMMARY
- Title
-
Vagus Topographic Map: Wandering through a gRAdient
- Authors
- Walker, L.J., Granato, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Cell
|
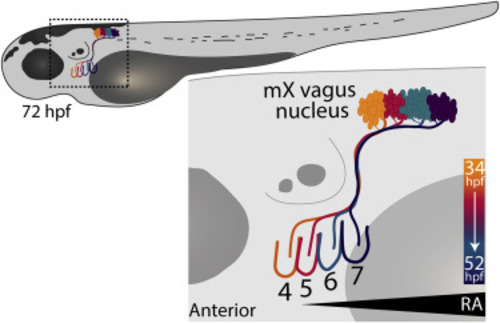
Figure 1. Topographic Mapping of mX Neurons to Pharyngeal Arches Schematic of a 72 h post fertilization (hpf) zebrafish larvae. Inset outlined in box highlights innervation of pharyngeal arches (PAs) 4–7 by vagus motor neurons (mX) within the spinal cord. Colors indicate both topographic mapping between mX neurons in the vagus nucleus and their relative PA targets and the approximate developmental time at which the mX axons are navigating. Concurrently, an anterior to posterior retinoic acid (RA) gradient recedes over time. |
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 53, Walker, L.J., Granato, M., Vagus Topographic Map: Wandering through a gRAdient, 257-258, Copyright (2020) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell