- Title
-
Endothelial Cell Dynamics in Vascular Development: Insights From Live-Imaging in Zebrafish
- Authors
- Okuda, K.S., Hogan, B.M.
- Source
- Full text @ Front. Physiol.
|
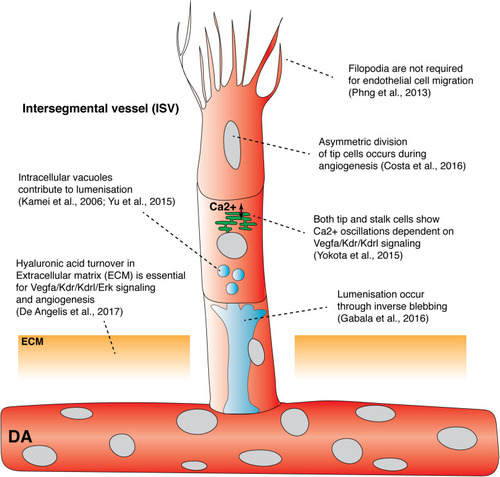
Recent findings from live imaging primary angiogenesis and lumenization in the zebrafish trunk. Recent studies have shown that asymmetric division of intersegmental filopodia have been shown to be dispensable vessel tip cells, hyaluronic acid turnover in extracellular matrix, and Ca2+ oscillation in both tip and stalk cells, drive primary angiogenesis. In contrast, filopodia has been shown to be dispensable for endothelial cell migration. Both vacuolar fusion and inverse blebbing have been proposed as mechanisms for lumenization in intersegmental vessels. DA, dorsal aorta; ECM, extracellular matrix; ISV, Intersegmental vessel. |
|
Recent findings from live imaging secondary angiogenesis/lymphatic sprouting in the zebrafish trunk. |
|
Recent findings from live imaging vessel remodeling and tip cell anastomosis in the zebrafish trunk. |