- Title
-
Functional and genetic analyses of ZYG11B provide evidences for its involvement in OAVS
- Authors
- Tingaud-Sequeira, A., Trimouille, A., Marlin, S., Lopez, E., Berenguer, M., Gherbi, S., Arveiler, B., Lacombe, D., Rooryck, C.
- Source
- Full text @ Mol Genet Genomic Med
|
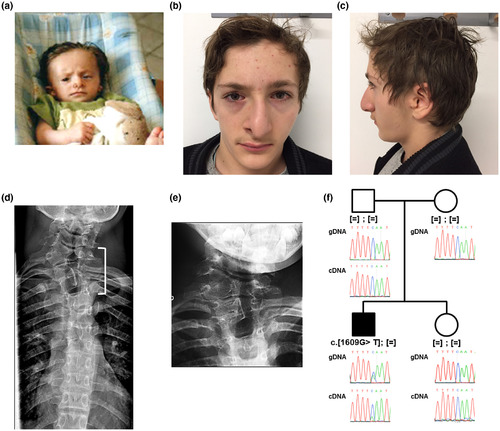
Photographs and pedigree of the patient carrying the c.1609G>T, p.(Gly537*) variant in ZYG11B. (a–c) Photographs showed the proband at infant stage (a) and at 15 years (b and c). (d) X‐ray imaging of patient vertebrae showing vertebral fusion of hypoplastic C7‐D1 vertebrae (white bracket). (e) Enlarged of C7‐D1 vertebrae. (f) Family tree and electrophoregrams showing the de novo heterozygous nonsense variant in the proband. Sequencing of RT‐PCR amplicons revealed that the transcript escapes to nonsense‐mediated RNA decay |
|
The nonsense variant encodes a mislocalized truncated ZYG11B protein. (a) Western blot validated overexpression experiments. (b) Immunocytochemistry detection of ZYG11B‐WT and ZYG11B‐E537* in HeLa cells. (c) RT‐qPCR experiments validated ZYG11B expression knockdown by the specific siRNA‐ZYG11B which also induced a significant down‐regulation of SOX6 expression, t test p < .05. (d) Cell proliferation is significantly decreased when treated with siRNA‐ZYG11B (Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunns’ post hoc multiple comparison test (p < .05)). (d) RT‐qPCR analysis of ZYG11B expression showed a down‐regulation following RA treatment in HeLa cells (t test p < .05) |
|
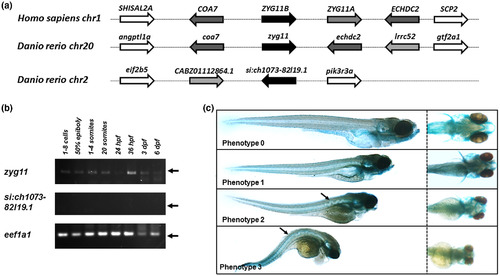
Zebrafish zyg11 gene knockdown impaired craniofacial cartilages and notochord development. (a) Conserved synteny between human ZYG11B genomic environment and zebrafish homologues. (b) expression pattern of zyg11 and si:ch1073‐82l19.1 genes in zebrafish by RT‐PCR. (c) At 120 hpf, embryos were classified in 4 phenotypes |