- Title
-
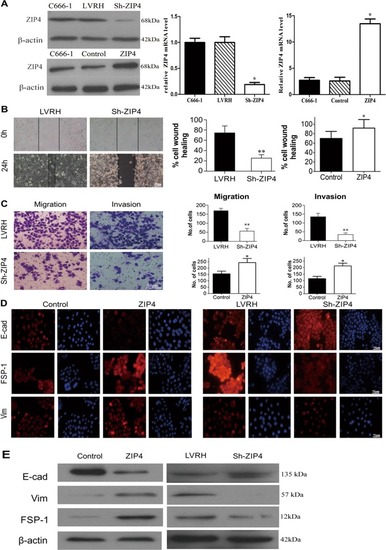
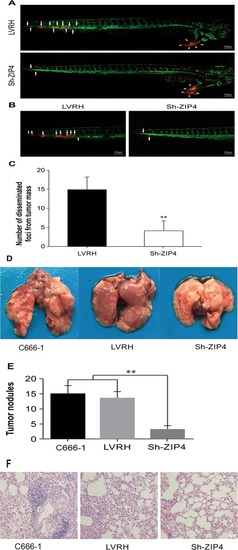
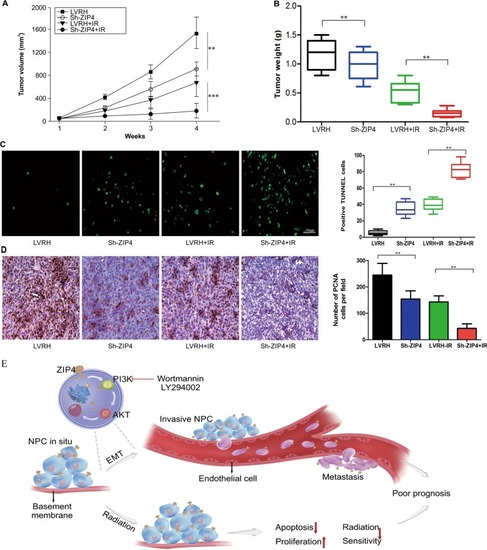
Inhibition of ZIP4 reverses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and enhances the radiosensitivity in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
- Authors
- Zeng, Q., Liu, Y.M., Liu, J., Han, J., Guo, J.X., Lu, S., Huang, X.M., Yi, P., Lang, J.Y., Zhang, P., Wang, C.T.
- Source
- Full text @ Cell Death Dis.
|
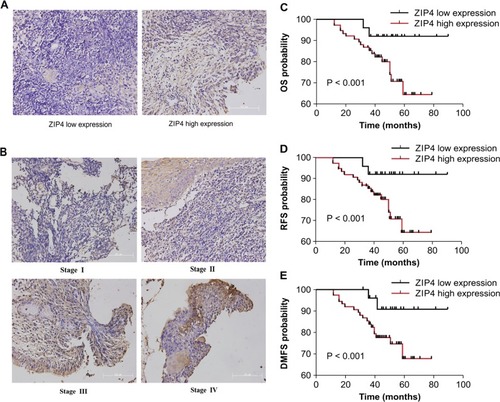
Representative specimens from patients with NPC showed weak ( |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|