- Title
-
NaV1.1 and NaV1.6 selective compounds reduce the behavior phenotype and epileptiform activity in a novel zebrafish model for Dravet Syndrome
- Authors
- Weuring, W.J., Singh, S., Volkers, L., Rook, M.B., van 't Slot, R.H., Bosma, M., Inserra, M., Vetter, I., Verhoeven-Duif, N.M., Braun, K.P.J., Rivara, M., Koeleman, B.P.C.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
A) 5 dpf PHENOTYPE:
|
|
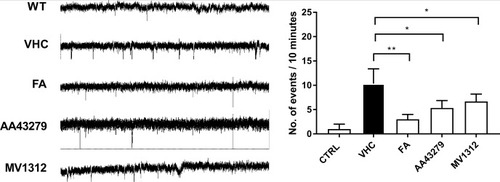
Only two types of signals can be detected in wildtype embryos: low amplitude waves and very occasional sharp single spikes from an otherwise straight and silent baseline (1 and 2). In PHENOTYPE:
|
|
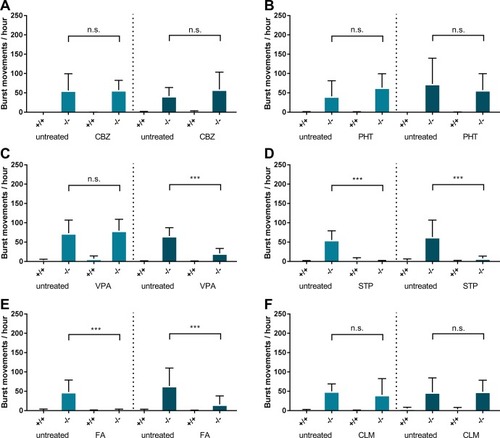
Dashed lines indicate a novel experimental plate with a seperate experimental group. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
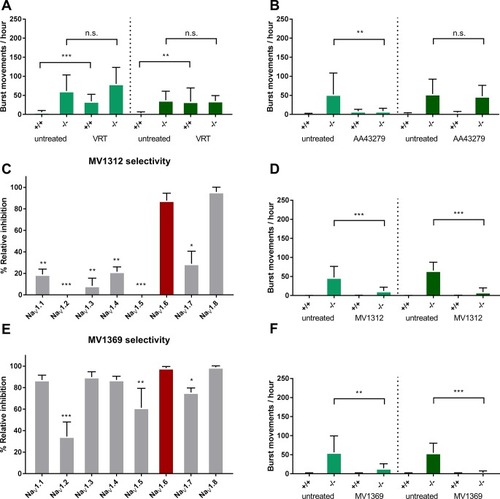
Characterization of novel compounds and their effect on PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Error bars = S.D n = 3 per group * <0.05 **<0.005. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
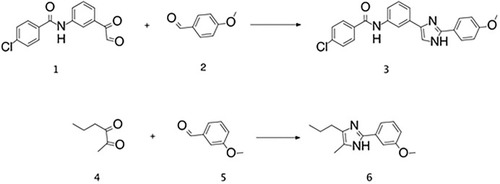
Overnight rt. |