- Title
-
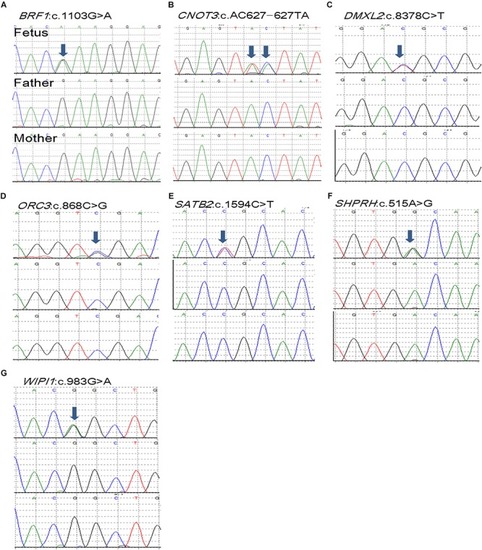
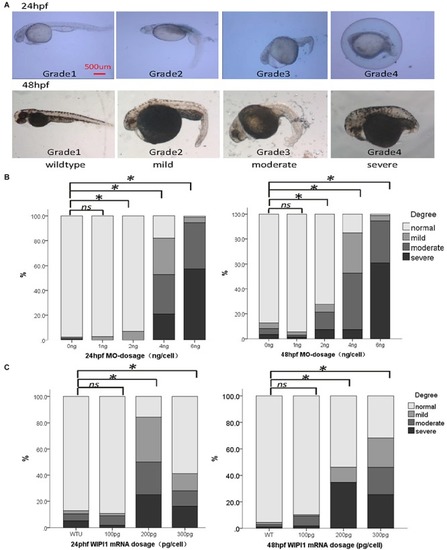
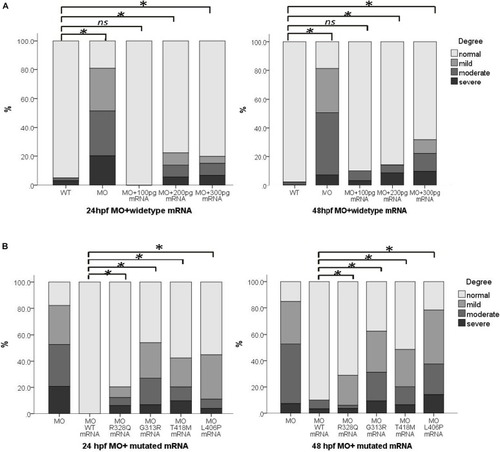
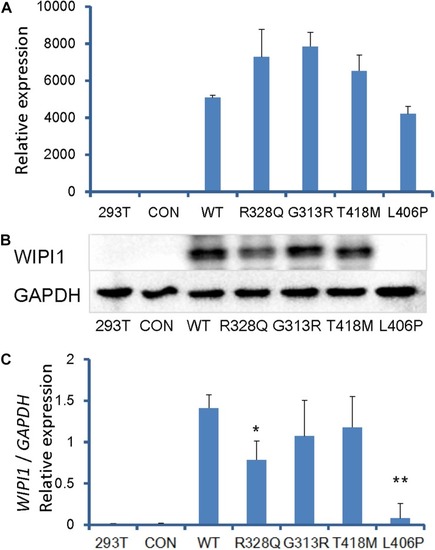
Whole-Exome Sequencing Identifies Damaging de novo Variants in Anencephalic Cases
- Authors
- Wang, L., Ren, A., Tian, T., Li, N., Cao, X., Zhang, P., Jin, L., Li, Z., Shen, Y., Zhang, B., Finnell, R.H., Lei, Y.
- Source
- Full text @ Front. Neurosci.
|
|
|
Abnormal expression of |
|
|
|
|