- Title
-
Inhibition of in-stent restenosis after graphene oxide double-layer drug coating with good biocompatibility
- Authors
- Ge, S., Xi, Y., Du, R., Ren, Y., Xu, Z., Tan, Y., Wang, Y., Yin, T., Wang, G.
- Source
- Full text @ Regen Biomater
|
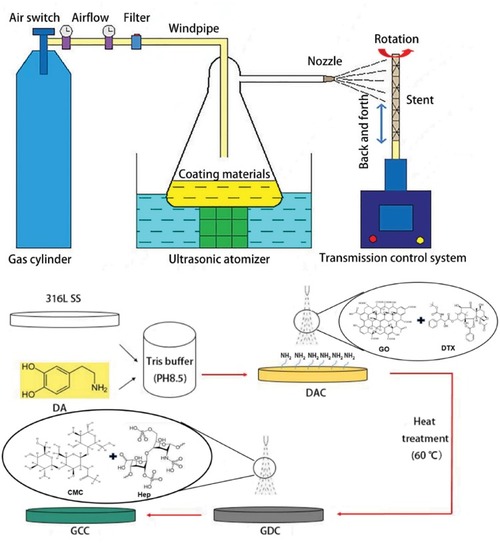
The coating processing and the CS-III pro-ultrasonic spray system [ |
|
GCC coating has minimum effects on surface roughness but significantly decreases water contact angle. ( |
|
GCC Coating exhibits superior blood compatibility. ( |
|
GDC and GCC Significantly inhibit the proliferation of VSMCs. VSMCs were plated on 316L SS coated with DAC, GDC or GCC. The images were taken at Days 1, 3 and 5, respectively ( |
|
Various coatings exhibit no detectable toxicity in the embryonic development of zebrafish. Zebrafish embryos were co-cultured with 316L SS, DAC, GDC and GCC stents for 24, 48 and 72 h, respectively. The morphology ( |
|
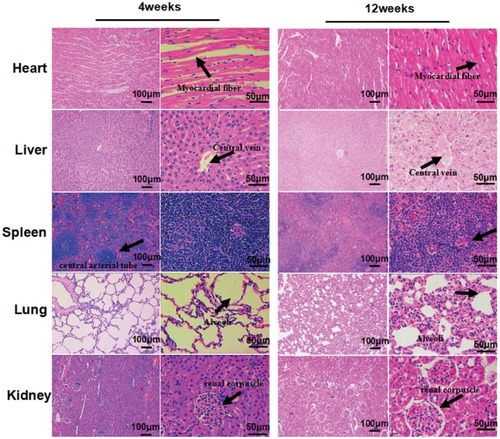
The GCC Stents have no significance effects on the main organs of rabbits at 4 and 12 weeks after implantation. The black arrows represent myocardial fiber, Central vein, Central arterial tube, alveoli and renal corpuscle |
|
The Endothelialization and restenosis of GCC stents. ( |