- Title
-
Zebrafish Models of Diamond-Blackfan Anemia: A Tool for Understanding the Disease Pathogenesis and Drug Discovery
- Authors
- Uechi, T., Kenmochi, N.
- Source
- Full text @ Pharmaceuticals (Basel)
|
Zebrafish DBA models. Wild-type embryos show a high density of red blood cells (WT), whereas the blood production is drastically reduced in the |
|
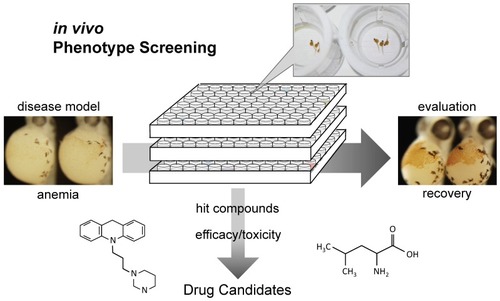
Zebrafish in vivo phenotype screening. Zebrafish provides a novel platform for screening compound libraries and evaluating drug efficacy in vivo, which will lead to find new therapeutics for rare diseases including DBA. |