- Title
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Neuroprotective Effects of Stellettin B Through Anti-Apoptosis and the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway
- Authors
- Feng, C.W., Chen, N.F., Wen, Z.H., Yang, W.Y., Kuo, H.M., Sung, P.J., Su, J.H., Cheng, S.Y., Chen, W.F.
- Source
- Full text @ Mar. Drugs
|
Cytoprotective effect of SB against 6-OHDA damage in SH-SY5Y cells: (A) SH-SY5Y cells were pretreated with 0.1, 1, 10, or 100 nM SB for 1 h and then challenged with 20 μM 6-OHDA for 16 h. Apoptosis in the 6-OHDA-treated group was normalized to 0%. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, and each value represents the mean of three replicates and six samples. * significantly different from the 6-OHDA group; (B) SH-SY5Y cells were pretreated with 0.1 nM SB for 1 h and then challenged with 20 μM 6-OHDA for 8 h. Hoechst 33342 stainings of the control, 6-OHDA, 6-OHDA plus SB, and SB alone groups are shown. The white arrows indicate the locations of chromatin condensation (scale bar = 100 μM); (C) Quantification of cytotoxicity in each group. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, and each value represents the mean of three replicates and three samples. *significantly different from the control group; # significantly different from the 6-OHDA group. p < 0.05 |
|
Cytoprotective effect of SB against 6-OHDA damage in SH-SY5Y cells: (A) SH-SY5Y cells were pretreated with 0.1, 1, 10, or 100 nM SB for 1 h and then challenged with 20 μM 6-OHDA for 16 h. Apoptosis in the 6-OHDA-treated group was normalized to 0%. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, and each value represents the mean of three replicates and six samples. * significantly different from the 6-OHDA group; (B) SH-SY5Y cells were pretreated with 0.1 nM SB for 1 h and then challenged with 20 μM 6-OHDA for 8 h. Hoechst 33342 stainings of the control, 6-OHDA, 6-OHDA plus SB, and SB alone groups are shown. The white arrows indicate the locations of chromatin condensation (scale bar = 100 μM); (C) Quantification of cytotoxicity in each group. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, and each value represents the mean of three replicates and three samples. *significantly different from the control group; # significantly different from the 6-OHDA group. p < 0.05 |
|
The anti-apoptotic effect of SB on 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells: SH-SY5Y cells were pretreated with 0.1 nM SB for 1 h and then challenged with 20 μM 6-OHDA for 8 h in the control, 6-OHDA, 6-OHDA plus SB, and SB alone treatment groups. (A) TUNEL staining. White arrows indicate apoptotic cells (scale bar = 100 μM); (B) Quantification of apoptotic cells in each treatment group; (C) Western blotting showing induction of cleaved caspase-3 protein; (D) Quantification of relative density of cleaved caspase-3 protein from Western blotting. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, and each value represents the mean of three replicates and three samples. *significantly different from the control group; # significantly different from the 6-OHDA group. |
|
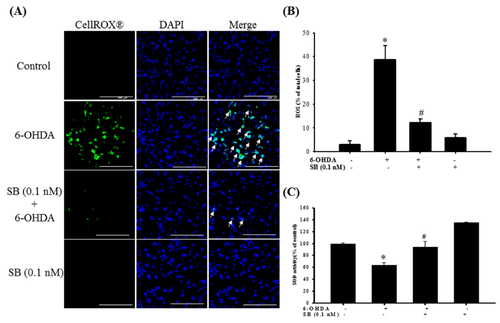
Effect of SB on 6-OHDA-induced upregulation of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and downregulation of superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. SH-SY5Y cells were pretreated with 0.1 nM SB for 1 h and then challenged with 20 μM 6-OHDA for 2 h. (A) CellROX® of the control, 6-OHDA, 6-OHDA plus SB, and SB treatment groups. White arrows indicate the location of ROS-positive cells (scale bar = 100 μM). (B) Quantification of the frequency of ROS-positive cells in each group. (C) SOD levels of the control, 6-OHDA, 6-OHDA plus SB, and SB alone treatment groups. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, and each value represents the mean of three replicates and three samples. *significant compared with the control group; # significant compared with the 6-OHDA group. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|