- Title
-
Using Zebrafish for Investigating the Molecular Mechanisms of Drug-Induced Cardiotoxicity
- Authors
- Zakaria, Z.Z., Benslimane, F.M., Nasrallah, G.K., Shurbaji, S., Younes, N.N., Mraiche, F., Da'as, S.I., Yalcin, H.C.
- Source
- Full text @ Biomed Res. Int.
|
Overview of zebrafish heart development. By 14 hpf, cardiac progenitors have emerged from the anterior lateral plate mesoderm. These cardiac precursors migrate and fuse at the midline to form a cone structure by 19 hpf. After one day of development, a beating linear heart tube has formed to propel circulation through the body. Cardiac chambers are clearly demarcated and looping has completed after two days of development.VM, ventricle myocardium; AM, atrium myocardium; EC, endocardium; (upper panel) stage of development and hour postfertalisation, hpf, and (lower panel) genes that regulate the developmental processes. Gata5, Transcription factor required during cardiovascular development; Hand2, Heart And Neural Crest Derivatives Expressed 2;Tbx20, T-Box Transcription Factor; Smarcd3,4, SWI/SNF Related, Matrix Associated, Actin Dependent Regulator Of Chromatin, Subfamily D, Member 3and 4; CTR1, copper transporter; Cdc37, Cell Division Cycle 37; RTF1, Paf1, LEO1, RNA Polymerase II Complex Component. |
|
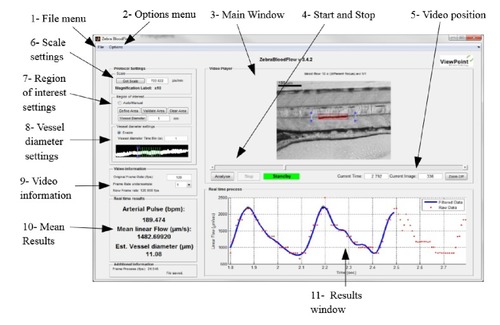
View point's ZebraLab software user interface. |
|
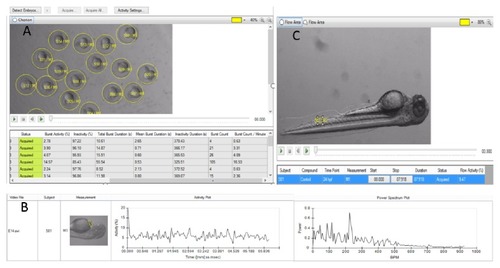
DanioScope system and EthoVision XT9.0 analysis platform. A. DanioScope recognizes the embryos and can analyze videos with multiple animals simultaneously and DanioScope reports back (table A) the following parameters: burst activity (percentage of time the embryo was moving), Inactivity (percentage of time of inactivity); burst duration (total time spent active); inactivity duration (total time spent inactive); burst count (number of times the embryo moved); Burst count/per minute. B. DanioScope measures activity in the heart of each larvae, from this activity the heartbeat in beats per second or per minute is extracted graph B. C. Flow activity can be measured in both blood vessels and the gut. |
|
Cardiotoxicity evaluation results adapted from Cornet et al. [ |
|
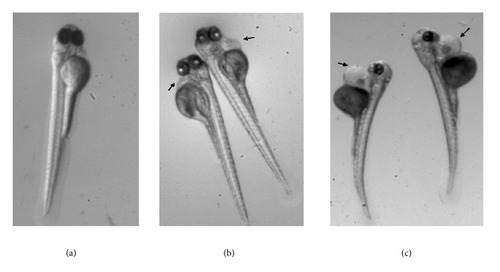
Magnification X= .63. Typical phenotype of a zebrafish embryo incubated from 24-hpf to 96-hpf in |