- Title
-
Perturbations of BMP/TGF-β and VEGF/VEGFR signalling pathways in non-syndromic sporadic brain arteriovenous malformations (BAVM)
- Authors
- Wang, K., Zhao, S., Liu, B., Zhang, Q., Li, Y., Liu, J., Shen, Y., Ding, X., Lin, J., Wu, Y., Yan, Z., Chen, J., Li, X., Song, X., Niu, Y., Liu, J., Chen, W., Ming, Y., Du, R., Chen, C., Long, B., Zhang, Y., Tong, X., Zhang, S., Posey, J.E., Zhang, B., Wu, Z., Wythe, J.D., Liu, P., Lupski, J.R., Yang, X., Wu, N.
- Source
- Full text @ J. Med. Genet.
|
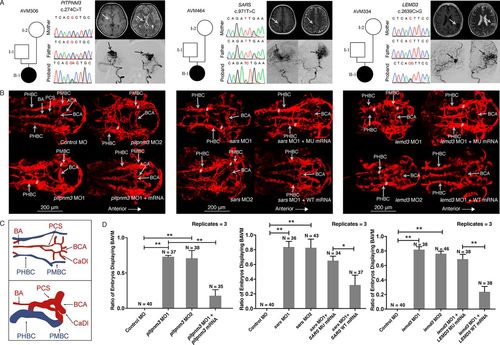
Variant information, phenotype and in vivo functional study of PITPNM3, SARS and LEMD3 variants in patient AVM306, AVM464 and AVM334. (A) Results of Sanger sequencing of the de novo variants in PITPNM3, SARS and LEMD3; brain MRI (BMRI) and digital subtraction angiography (DSA) demonstrating the arteriovenous malformation (arrows) in patient AVM306, AVM464 and AVM334. (B) Confocal imaging (dorsal view, anterior to the right) of Tg(kdrl.4:mCherry)pku6 transgenic fish injected with 5 ng of control morpholino or 5 ng of morpholino targeting pitpnm3, sars or lemd3 at 48 hours postfertilisation (hpf). sars and lemd3 morphants were then coinjected with 200 pg of human mRNA. Note the basilar artery (BA), basal communicating artery (BCA), anterior cerebral artery (ACA), metencephalic arteries (MtA), primordial hidbrain channel (PHBC), primordial midbrain channel (PMBC) and posterior connecting segments (PCS). AVMs of BA/PHBC or BCA/PMBC is labelled with ‘#’. (C) Wiring diagrams of BAVM in 48 hpf compared with normal brain vessels. Red wires represent arteries; blue wires represent veins. (D) Significant difference existed between the percentage of embryos displaying BAVM phenotype between pitpnm3 morphants (MO1: 73%, 27/37; MO2: 68%, 26/38) and control embryos (0%) (Student’s t-test, MO1: p=0.00000037; MO2: p=0.0082). Coinjection of pitpnm3 MO2 and pitpnm3 mRNA resulted in reduced percentage of BAVM embryos (17%, 6/35, p=0.00043). Percentage of embryos exhibiting a BAVM-like phenotype between sars morphants (MO1: 83%, 30/36; MO2: 79%, 34/43) and control embryos (0%) was significantly different (Student’s t-test, MO1: p=0.000045; MO2: p=0.00025). BAVM-like phenotype was rescued by human wild-type SARS mRNA (41%, 15/37) but not mutant SARS mRNA (74%, 25/34) (Student’s t-test, p=0.018). A significant difference in the percentage of embryos exhibiting BAVM-like phenotype was detected between the lemd3 morphants (MO1: 82%, 31/38; MO2: 76%, 35/46) and control embryos (0%) (Student’s t-test, MO1: p=0.00094; MO2: p=0.00075). The BAVM-like phenotype was rescued by human wild-type LEMD3 mRNA (24%, 9/38) but not mutant LEMD3 mRNA (66%, 25/38) (Student’s t-test, p=0.0015). Error bars represent one SD, n=3 replicates. A different clutch of embryos was used for each replicate. *P<0.05; **p<0.01. BAVM, brain arteriovenous malformation; MO1, morpholino targeting splice site; MO2, morpholino targeting AUG start codon site; MU, mutant; WT, wild-type. PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|