- Title
-
Highly efficient transduction of primary adult CNS and PNS neurons
- Authors
- Levin, E., Diekmann, H., Fischer, D.
- Source
- Full text @ Sci. Rep.
|
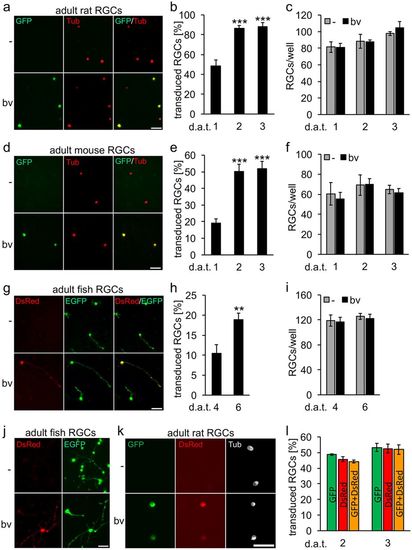
Dissociated retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) isolated from adult rats (a–c), mice (d–f) and zebrafish (g–i) were transduced with baculovirus (bv) encoding fGFP (rat and mice) or DsRed (zebrafish). Representative pictures of vehicle- (-) and bv -treated cultures (a,d,g) visualize transduced RGCs (GFP and DsRed, respectively) that were either co-stained with the neuronal marker βIII-tubulin (Tub, red) at 2 days after transduction (d.a.t) for rat and mice RGCs (a,d) or identified by EGFP expression for zebrafish RGCs at 6 d.a.t. (g). The percentage of transduced RGCs was determined at 1, 2 and 3 days after transduction (d.a.t.) for rat and mice (b,e) and at 4 and 6 d.a.t. for zebrafish (h). Treatment effects compared to vehicle-treated controls: ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01. Scale bars: 50 μm. RGC survival (c,f,i) was not affected by baculovirus application (bv) compared to vehicle-treated controls (-). (j) Delayed transduction of adult zebrafish RGCs with DsRed-bv after 4 days in culture. Scale bar: 50 μm. (k,l) Co-transduction of adult rat RGCs with fGFP-bv and DsRed-bv. The two viruses were added to retinal cultures simultaneously at half the concentration of single transductions. Representative pictures show co-transduced, fGFP- and DsRed-expressing RGCs (green and red, respectively) that were co-stained against the neuronal marker βIII-tubulin (white) at 2 d.a.t. Scale bar: 50 μm. (k). The percentage of transduced RGCs was determined at 2 and 3 d.a.t. (l). Non-significant difference in co-tranduction efficiency compared to single transductions. |