- Title
-
Embryonic bone morphogenetic protein and nodal induce invasion in melanocytes and melanoma cells
- Authors
- Sinnberg, T., Niessner, H., Levesque, M.P., Dettweiler, C., Garbe, C., Busch, C.
- Source
- Full text @ Biol. Open
|
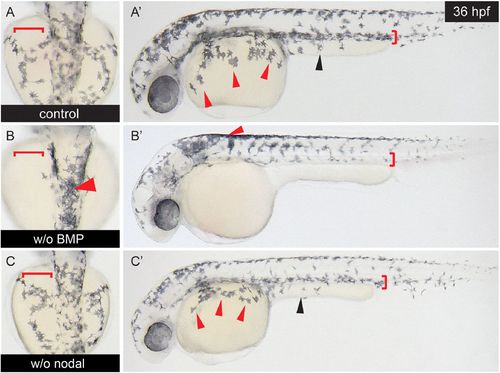
Blocking of BMP signaling, but not of nodal signaling, inhibits autochthonous neural crest migration in zebrafish embryos. Zebrafish embryos (n=6 per group) were exposed to 10 µM of the BMP type I receptor-antagonist dorsomorphin or to 30 µM of the Alk4/5/7 nodal receptor antagonist SB431542 6 hpf. Embryos at 36 hpf were analyzed for neural crest cell migration. (A,A′) Control embryos show a normal pattern of neural crest cell migration along the dorsolateral and the dorsoventral migration pathways in upper and lateral view. (B,B′) Upon dorsomorphin treatment neural crest migration is impaired along both pathways. (C,C′) SB431542 does not influence neural crest migration in zebrafish embryos. Arrowheads indicate melanocytes that are supposed to populate the yolk sac (red arrowheads) or the yolk extension (black arrowheads). The areas into which the melanocytes migrate by the dorso-ventral or dorso-lateral pathways are marked by red brackets. PHENOTYPE:
|