- Title
-
Variant Histone H2afv Reprograms DNA Methylation During Early Zebrafish Development
- Authors
- Madakashira, B., Corbett, L., Zhang, C., Paoli, P., Casement, J.W., Mann, J., Sadler, K.C., Mann, D.A.
- Source
- Full text @ Epigenetics
|
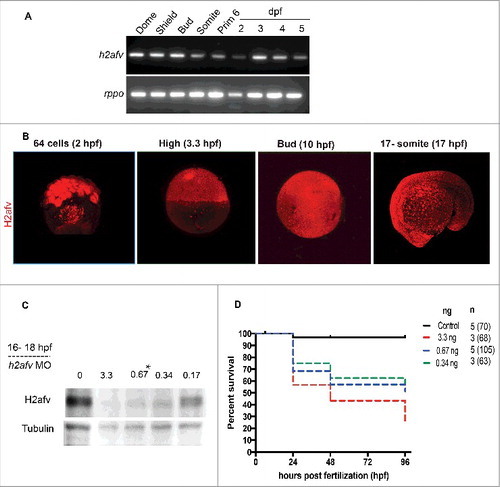
H2afv expression successfully depleted by morpholino (MO) injection (A) RT-PCR using primers that detect both h2afva and h2afvb demonstrates high mRNA levels of expression across all stages of embryonic zebrafish development. (B) Whole mount immunofluorescence detects H2afv protein expression across stages of zebrafish embryonic development. Representative images from at least 5 embryos examined from 2 separate clutches are shown. (C) Western blot analysis demonstrates depletion of H2afv expression at 24 hpf in lysates from varying concentrations of h2afv MO injected embryos compared with control (uninjected) embryos. h2afv morphants (0.67 ng) were used for the rest of the study (marked*). Representative image of 2 different blots are shown. (D) Kaplan-Meier curve illustrates increased mortality of h2afv morphants compared with control (uninjected) embryos across 96 h post fertilization (hpf). MO injected at 3.3, 0.67 and 0.34 ng per embryo, n = number of clutches and number of total embryos analyzed per condition in parenthesis. |
|
H2afv depletion causes significant phenotypic abnormality (A) Bright field images comparing Control (uninjected) and h2afv MO injected fish at 24 and 48 hpf, with the same embryo imaged at both time points. (B) Embryos were scored as Severe, Mild or Normal phenotype in a minimum of 5 clutches and displayed as percentages, with n = the number of total embryos and the number clutches analyzed per condition. (C) Western blot analysis of 24 hpf embryos demonstrates complete depletion of the H2afv protein in morphants exhibiting the severe phenotype and slight residual protein expression in h2afz morphants with mild phenotype while the control (uninjected) embryos express high levels of H2afv protein. (D) Bright field images of 48 hpf embryos injected with h2afv mRNA (50 ng), h2afv MO or h2afv mRNA plus h2afz MO. Phenotypic normality is restored in co-injected embryos. (E) Phenotype percentages of h2afv MO or h2afv mRNA injected with control morpholino-1 or with h2afz morpholino scored at 48 hpf. Scale bar: 1000 μm. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Co-injection of dnmt1 MO partially rescues the h2afv morphant phenotype (A) Bright field images comparing embryos injected with control morpholino-2 (0.67 ng) or with h2afv (0.67 ng), dnmt1 (0.43 ng) or dnmt1-h2afv co injected embryos exhibiting the severe phenotype at 24 and 48 hpf. The dnmt1 morphants do not exhibit any significant phenotype either at 24 hpf or 48 hpf (n = 5) (B) Phenotype scored in a minimum of 5 clutches as Severe, Mild or Normal and displayed as percentages show that the percentage of h2afv morphants exhibiting the severe phenotype is significantly reduced in a dnmt MO background. (C) Percent survival of h2afv morphants with and without addition of dnmt1 MO at 24 hpf and 48 hpf. The survival of the h2afv morphants is not significantly affected with knockdown of Dnmt1 protein (p-value between the dead vs. alive numbers of h2afv and dnmt1- h2afv double morphants at 24 hpf = 0.4855 and at 48 hpf = 0.05. (D) Western blot analysis of protein lysates of 16-18 hpf embryos demonstrates complete depletion of the H2afv protein in both h2afv morphants and dnmt1- h2afv morphants while the expression of H2afv protein is unaffected in control and dnmt1 morphant embryos (n = 2). (E) Slot blot analysis of 5-MeC levels using genomic DNA from control, h2afv morphants and dnmt1- h2afv morphants at 14-18 somite stage (16-18 hpf). The h2afv morphants exhibit significant hypermethylation and the inhibition of dnmt1 in this background does not have a significant effect on the global DNA hypermethylation. One way ANOVA was performed comparing each of the morphants with the uninjected controls. Number of clutches (n) = 4. Scale bar: 1000 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
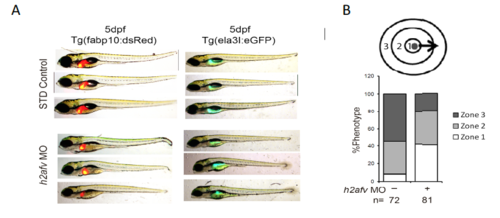
h2afv morphants display multi- systemic abnormalities (A) Bright field images of 5 dpf (120 hpf) Tg(fabp10:dsRed) and Tg(ela31:eGFP) control uninjected and h2afv MO injected into single-cell embryos. (B) Motility is severely affected in the h2afv morphants at 48 hpf. |
|
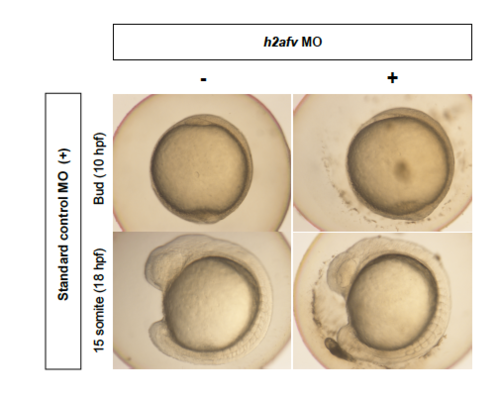
h2afv morphants do not exhibit any overt morphological phenotype by 18 hpf. Embryos injected with standard control MO 1, h2afv MO or standard control MO 1 + h2afv MO were examined for morphological changes at the bud stage (10 hpf) and at the 13-15 somite stage (16-18 hpf) by bright field microscopy. At both the early stages examined, the morphants were phenotypically indistinguishable from their control morpholino injected controls, indicating that the onset of the phenotype occurs later than 18 hpf. Images are representative of over 300 embryos observed from over 5 clutches. |
|
h2afva mRNA rescues the h2afv morphant phenotype. (A) Fish were injected with mCherry tagged h2afva mRNA that has been mutated to a 4 base mis-match with the morpholinos sequence and visualized by fluorescent microscopy at 24 hours in comparison to non- injected controls. (B) Western blot analysis of H2afv and H2afv-mCherry in 48 hpf lysates from fish injected with h2afv MO, h2afv mRNA, h2afv MO + mRNA or standard control MO 1. |
|
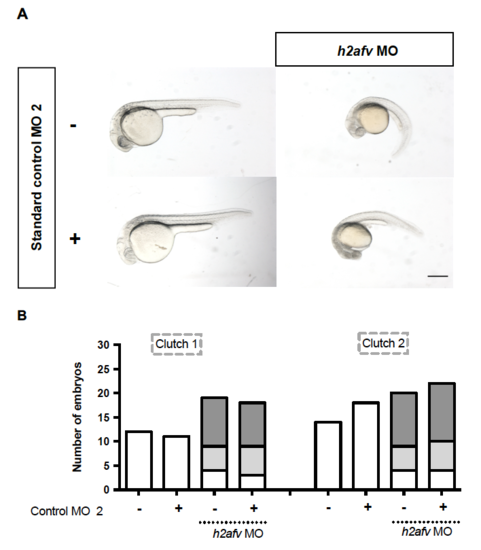
The h2afv morphant phenotype is unaffected by co-injection with standard control morpholino. (A) Fish embryos were injected with standard control MO 2, h2afv MO or standard control MO 2 + h2afv MO and were scored for phenotype at 24 hpf by bright field microscopy. Both the uninjected and standard control MO 2 were identical. Injection of h2afv MO along with the standard control MO 2 elicited the same phenotype as seen with h2afv MO alone, confirming that the phenotype is specifically due to the loss of H2afv protein. Scale bar: 1000 μm. (B) Analysis of the number of the h2afv morphants with and without addition of standard control MO 2 at 24 hpf. The control MO injection (0.67 ng) alone does not elicit any overt phenotype and its addition in h2afv morphants does not cause a change the phenotype caused by the h2afv morpholino. |
|
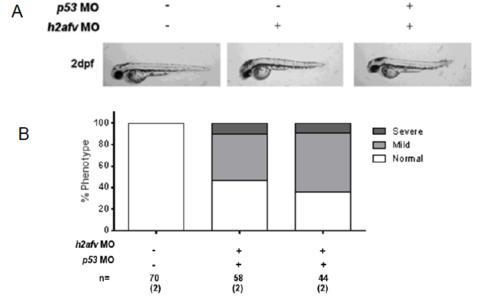
The h2afv morphant phenotype is unaffected by co-injection with a morpholino targeting tp53. (A) Fish injected with standard control MO 1, h2afv MO or h2afv + p53 MO were scored for phenotype at 2 dpf by bright field microscopy. (B)Phenotypes were scored at 2 dpf. n indicates total number of embryos scored and the number of clutches analyzed is indicated in parenthesis. |