- Title
-
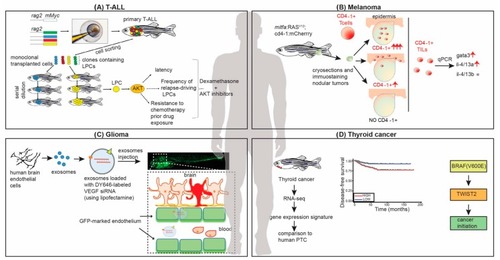
Zebrafish in Translational Cancer Research: Insight into Leukemia, Melanoma, Glioma and Endocrine Tumor Biology
- Authors
- Idilli, A.I., Precazzini, F., Mione, M.C., Anelli, V.
- Source
- Full text @ Genes (Basel)
|
Novel aspects of tumor biology and translational approaches using zebrafish models. ( |