- Title
-
Characterization of the Zebrafish Homolog of Zipper Interacting Protein Kinase
- Authors
- Carr, B.W., Basepayne, T.L., Chen, L., Jayashankar, V., Weiser, D.C.
- Source
- Full text @ Int. J. Mol. Sci.
|
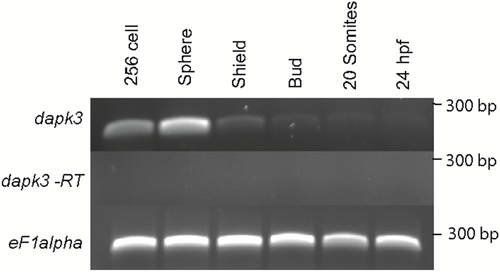
Temporal expression of zipk (dapk3) during early zebrafish development. Gene specific primers were used to detect zipk (286 bp) in various stages of development by RT-PCR. The zipk mRNA was expressed maternally and zygotically throughout early development. Amplification of eF1 alpha and total RNA without addition of reverse transcriptase were used as controls. |
|
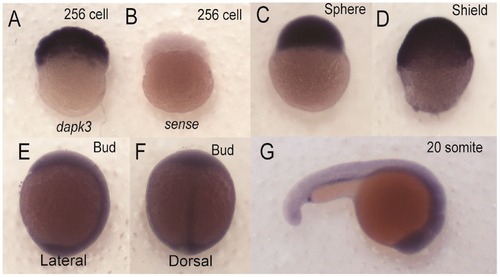
Spatial expression of zipk (dapk3) during early zebrafish development. Detection of zipk mRNA (dapk3) was carried out by whole-mount in situ hybridization using gene-specific probes on staged embryos at the 256 cells stage (A); sphere stage (C); shield stage (D); bud stage ((E) lateral view and (F) dorsal view); 20 somite stage (G); Negative control sense probes for zipk did not show staining at the 256 cell stage (B) or other stages (data not shown). Because of the difference in expression maternal stages (A–C) were developed for a shorter time than zygotic stages (D–G). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
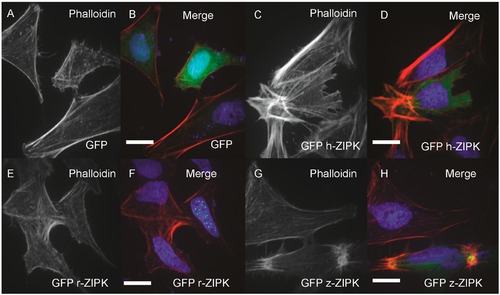
Differential regulation of the actin cytoskeleton by ZIPK homologs. HeLa cells were transfected with either GFP alone (A, B); human GFP-ZIPK (C, D); rat GFP-ZIPK (E, F); zebrafish GFP-ZIPK (G, H). All cells were fixed and stained with DAPI and Alexa 568-phalloidin and imaged with confocal microscopy. Black and white images show phalloidin staining, while color images are a merge of DAPI (blue), GFP (green) and phalloidin (red). Each experiment was replicated a minimum of five times with at least 25 cells assayed per experiment. White bar indicates 20 μm. |
|
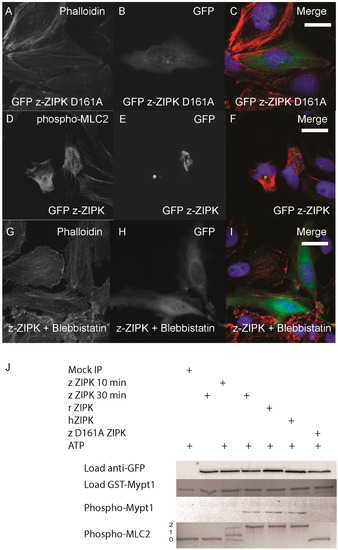
Zebrafish ZIPK controls the actin cytoskeleton by regulating type-II myosin (MLC2) phosphorylation. HeLa cells were transfected with a kinase dead D161A zebrafish GFP-ZIPK (A, B, C) and fixed and stained with DAPI and Alexa 568-phalloidin; HeLa cells were transfected with a zebrafish GFP-ZIPK (D, E, F) and immunostained using an anti-phospho myosin light chain 2 antibody, co-stained with DAPI; HeLa cells were treated with media containing either 0.1% DMSO (not shown) or 50 µM blebbistatin (G, H, I) for 4 h; Black and white images show phalloidin staining, while color images are a merge of DAPI (blue), GFP (green), and phalloidin (red). (J) Zebrafish, Rat and Human ZIPK immunoprecipitated from HEK 293T cells were used to phosphorylate purified GST-Mypt1 and GST-MLC2. Unphosphoryled (0), mono (1) and di-phosphorylation (2) MLC2 was detected by band shift using a phos-tag SDS-PAGE gel and stained with Coomassie. Phosphorylation of Mypt1 was detected using a phospho-specific antibody (T696). Each experiment was replicated a minimum of three times. White bar indicates a 20 μm scale bar. |
|
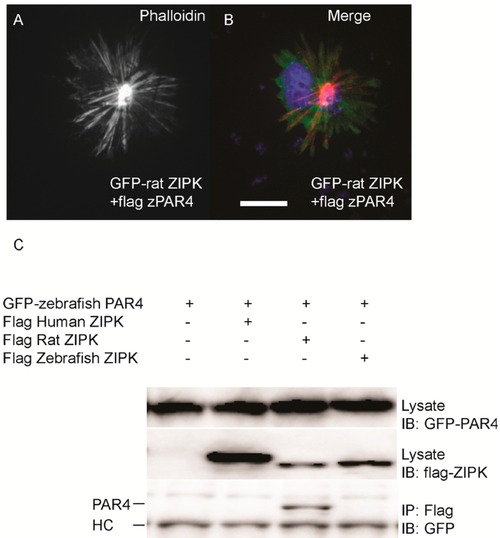
Differential interaction of ZIPK homologs with zebrafish PAR-4. HeLa cells were transfected with rat GFP-ZIPK and flag zebrafish PAR-4 (A, B). The cells were fixed and stained with DAPI and Alexa 568-phalloidin. Black and white images show phalloidin staining, while color images are a merge of DAPI (blue), GFP (green), and phalloidin (red).White bar indicates a 20 μm scale; (C) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with GFP-tagged zebrafish PAR-4 along with flag-tagged ZIPK from human, rat and zebrafish. Protein complexes were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibodies. The IPs were immunoblotted with anti-GFP antibodies and anti-FLAG antibodies. HC indicates the IgG heavy chain which is the same size as zebrafish and mouse ZIPK, while human is slightly heavier. Each experiment was repeated a minimum of three times. |
|
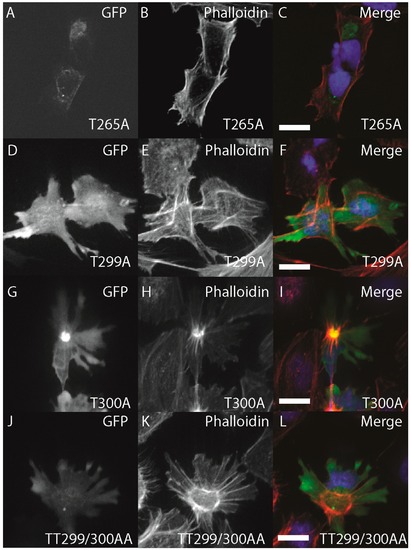
Structure-function of zebrafish ZIPK. HeLa cells were transfected with either GFP-ZIPK constructs generated by site-directed mutagenesis mutating a proposed activating phosphorylation site T265 or phosphorylation sites involved in controlling subcellular localization in the human paralog T299 and T300. All cells were fixed and stained with DAPI and Alexa 568-phalloidin. (A, D, G, J) show phalloidin staining; (B, E, H, K) show GFP; while color images (C, F, I, L) are a merge of DAPI (blue), GFP (green) and phalloidin (red). Each experiment was performed at least five times with a minimum of 25 cells assayed per experiment. White bar indicates 20 μm. |
|
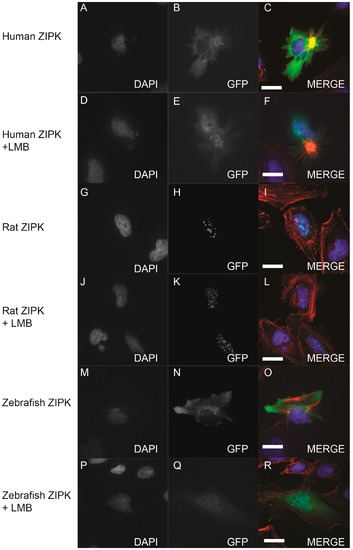
Nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of zebrafish ZIPK. HeLa cells were transfected with either human GFP-ZIPK (A–F); rat GFP-ZIPK (G–L); or zebrafish GFP-ZIPK (M–R). All cells were fixed and stained with DAPI and Alexa 568-phalloidin. The cells in (A–C, G–I, M–O) were treated with 0.1% DMSO; while the cells in (D–F, J–L, P–R) were treated with 50 nM leptomycin B for four hours. (A, D, G, J, M, P) are stained with DAPI; (B, E, H, K, N, Q) show subcellular localization of the GFP-fusion protein, while color images are a merge of DAPI (blue), GFP (green), and phalloidin (red). Each experiment was repeated three times with a minimum of 25 cells assayed per experiment. White bar indicates 20 μm. |