- Title
-
Probiotic Supplementation Promotes Calcification inDanio rerio Larvae: A Molecular Study
- Authors
- Maradonna, F., Gioacchini, G., Falcinelli, S., Bertotto, D., Radaelli, G., Olivotto, I., and Carnevali, O.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
Skeletal development in zebrafish using alcian blue-Alizarin red double staining. A 9 dpf zebrafish control larvae head skeleton presenting calcified calcified pharyngeal teeth (CPT)while other structures like Meckel′s cartilage (MC) and ceratohyal (CH) remain as cartilage); (B–C) 9 dpf control zebrafish head (B) and trunk (C) presenting no signals of bone calcification.(A) A 9 dpf L. rhamnosus fed zebrafish larvae head skeleton presenting calcification of the opercula (OP), cleithrum (CL) and basioccipital articulatory process (BOP). Meckel′s cartilage (MC) and ceratohyal (CH) remain as cartilage; (E) 9 dpf L. rhamnosus fed zebrafish presenting the first hypurals (HYP) developing. Scale bar: 30 μm. |
|
Whole mounts double staining of the skeleton in larvae sampled at 16 dpf. (A–D) Images showing significant aspects of skeleton development in control zebrafish larvae. (B) Formation of first vertebrae (V). (D) Caudal hypuralia aquires final number of structures with modified hemal arches (MHA) and caudal fin rays (CR). (E–H) representative images showing the development of the skeleton in zebrafish fed L. rhamnosus. (E) presence of calcified pharyngeal teeth (PT) and ceratohyal (CH). (F–G) Vertebrae formation (in an anterior-posterior direction) toward the posterior end of the notochord. Formation of the first neural arches (NA) is observed dorsally in the anterior vertebrae. (H) Beginning of calcification of the hypurals (HYP) under the urostyle (UR) and presence of calcified caudal fin rays. Scale bar: 30 μm. |
|
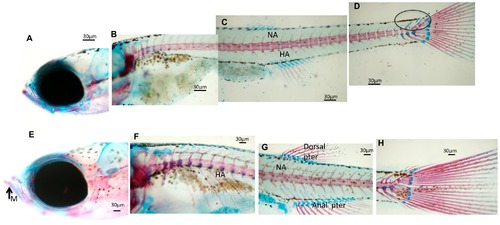
Whole mount double staining of the skeleton in larvae sampled at 23 dpf. (A–D) Images showing significant aspects of skeleton development in control zebrafish larvae. Neural arches (NA) and sketches of hemal arches (HA) are evidenced. Caudal skeleton still presents cartilaginous structures evidenced by a circle. (E–H) Representative images showing the development of the skeleton in zebrafish fed L. rhamnosus. (E) Presence of calcified mandibular (M). Neural arches (NA) and hemal arches (HA) are detected in the whole trunk of the larvae. (G) Complete formation of dorsal and anal pterygium.(H) Caudal skeleton is complete. Scale bar: 30 μm. |
|
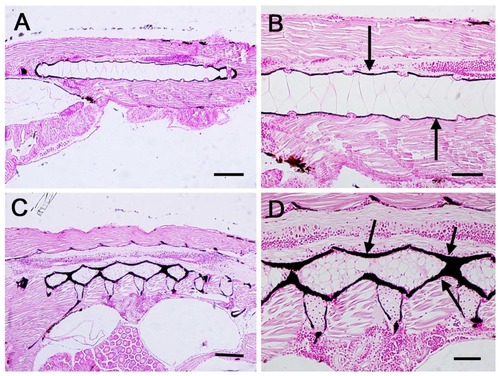
Von Kossa histochemical staining in larvae samples at 23 dpf. (A) Control zebrafish larva showing the mineral deposits around the notochord. (B) Higher magnification of image A. Arrows indicate the mineral deposits. (C) L.rhamnosus treated larva showing the mineral deposits around the vertebral bodies. (D) Higher magnification of image C. Arrows indicate the mineral deposits. Scale bars: A–C = 100 μm; B–D = 40 μm. |