- Title
-
Continual and partial MEK inhibition ameliorates cardio-facio-cutaneous phenotypes in zebrafish
- Authors
- Anastasaki, C., Rauen, K.A., and Patton, E.E.
- Source
- Full text @ Dis. Model. Mech.
|
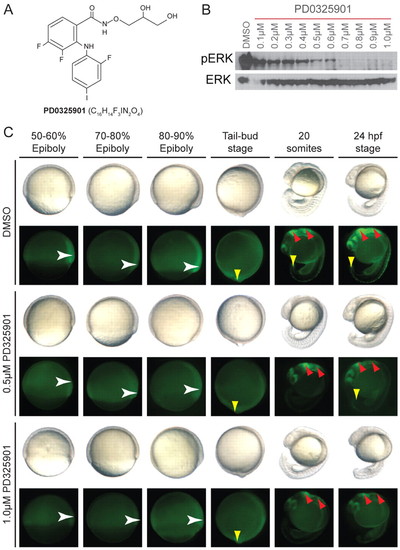
PD0325901 is an effective MEK inhibitor in zebrafish development. (A) Chemical structure of the selective MEK inhibitor PD0325901. (B) Western blot of 10-hpf zebrafish embryos treated with increasing concentrations of PD0325901 from 4 hpf, and immunostained with anti-phospho-ERK1/2 and anti-ERK1/2 antibodies. (C) Images of developing zebrafish treated with DMSO, or 0.5 μM or 1.0 μM PD0325901. Zebrafish were imaged under brightfield lighting conditions (top row), or using fluorescence microscopy to visualise GFP expressed from the dusp6 promoter (dusp6-GFP; bottom row). GFP signal was first detected in gastrulating embryos at 50–60% epiboly (white arrowhead). The expression area expanded towards the vegetal pole during epiboly (white arrowhead) and at the tail-bud stage the expression was more diffused with higher expression levels at the tail bud (yellow arrowhead). By 24 hpf, GFP expression was detected in the brain (red arrowhead), along the spinal column and in the tail bud (yellow arrowhead). n=30 embryos per treatment condition. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
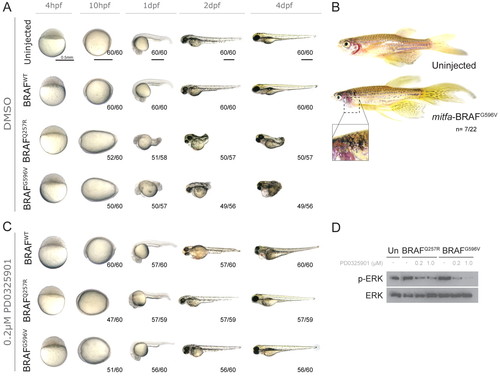
Continuous suboptimal PD0325901 treatment prevents zebrafish BRAFCFC phenotypes. (A) Wild-type embryos were injected with human BRAFWT, the kinase-activating and most common CFC allele BRAFQ257R, or the kinase-inactivating BRAFG596V, and imaged at the indicated developmental time post-fertilisation. (B) Images of untreated control zebrafish (top panel) and a zebrafish expressing the kinase-inactivating BRAFG596V allele under the melanocyte-specific mitfa promoter (bottom panel). Insert image depicts a high-magnification image of ectopic melanisation and nevi formation. (C) Continuous treatment of BRAFWT- and BRAFCFC-injected embryos with a suboptimal dose (0.2 μM) of PD0325901 from 4 hpf through 4 dpf. (D) Western blot of 10-hpf wild-type [uninjected (Un)] or BRAFCFC embryos treated with 0.2 μM of PD0325901 from 4 hpf, and immunostained with anti-phospho-ERK1/2 and anti-ERK1/2 antibodies. |
|
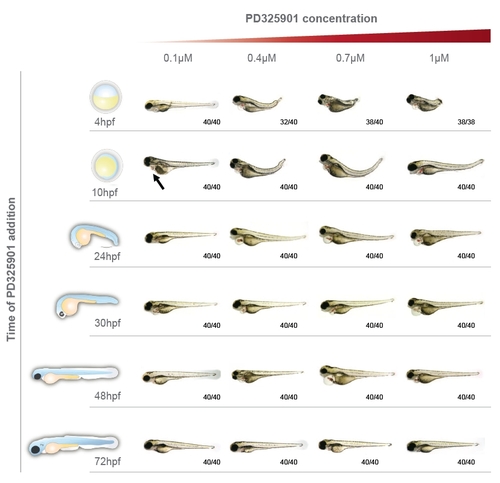
MEK inhibition promotes body axis defects. MEK inhibition promotes body axis defects. Images of 4 dpf zebrafish embryos treated with increasing concentrations of PD0325901 from 4 hpf to 72hpf. Schematic representations of the embryonic stage at the time of treatments are shown. The numbers of embryos displaying the body axis phenotype are indicated. Some ariability was observed with the onset of oedema (arrow). |
|
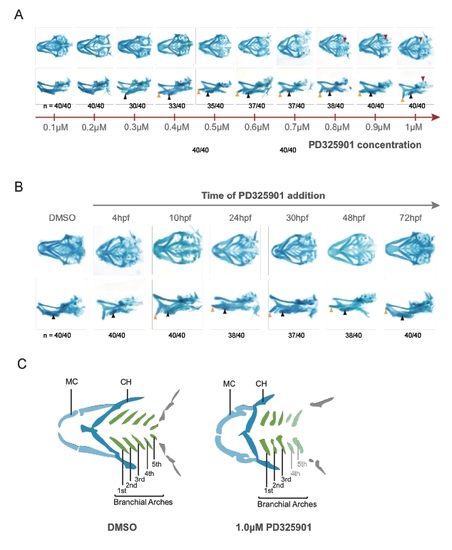
Craniofacial structures after PD0325901 treatments. A. Craniofacial structures of the 96 hpf zebrafish stained with Alcian blue after administration of increasing concentrations of PD0325901 (0.1-1.0 μM) from 4 hpf. Craniofacial cartilages were dissected from the body and additional tissues removed for imaging. Meckel’s cartilage (orange arrowheads), ceratohyal cartilage (black arrowheads), and pharyngeal arches (red arrowheads) are indicated. B. Comparison of craniofacial cartilage of 4 day old control embryos (DMSO) and embryos treated with 1 μM PD0325901 added at the indicated timepoints in development (4 - 72 hpf). Meckel’s cartilage (orange arrowheads) and ceratohyal cartilage (black arrowheads) are indicated. The numbers of embryos displaying the presented phenotype are indicated. C. Simplified, illustrative comparison of 4 dpf zebrafish jaw structures after control or intensive PD0325901 treatments 4 hpf (ventral view). High concentrations of the MEK inhibitor cause structural malformation, distortion of the angle between Meckel’s and ceratohyal cartilages and complete lack of the 4th and 5th branchial arches. The seven pharyngeal arches represented are: MC: Meckel’s cartilage (light blue); CH: ceratohyal cartilage (dark blue); 1st-5th branchial arches (green), fins (grey). |
|
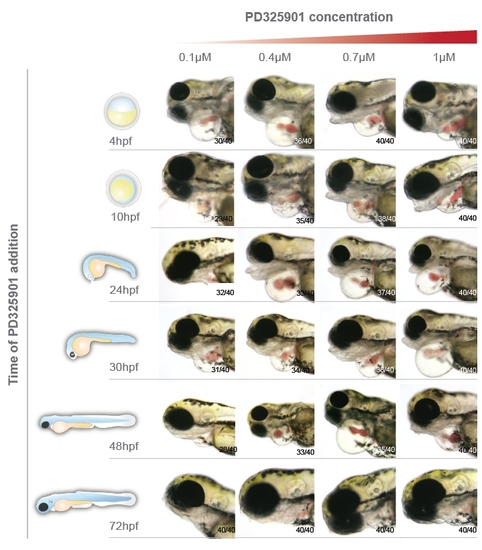
heart development after PD0325901 treatments. Lateral views of 4 dpf embryos treated with increasing concentrations of PD0325901. Addition of the inhibitor, even at low concentrations (0.1 μM) blocked the cardiac valve and blood remained restricted in the heart chambers. Cardiac oedemas were frequently observed. Blood circulation of embryos treated at 3 dpf was not affected at 4 dpf, but continual follow-up showed that these embryos eventually developed heart oedemas with variable time of onset. The numbers of embryos displaying the heart phenotype are indicated. |
|
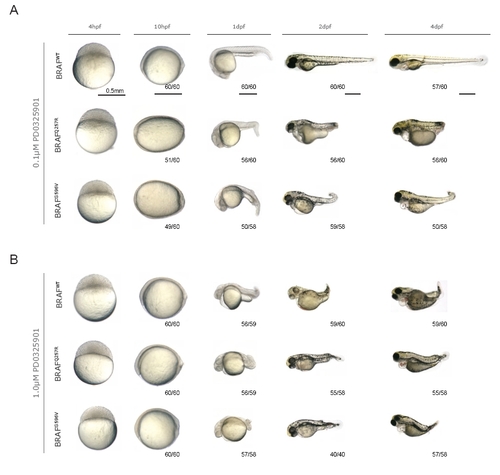
Continuous PD0325901 treatments of BRAFWT and BRAFCFC zebrafish. A. Wild type embryos were injected with human BRAFWT, the kinase-activating and most common CFC allele BRAFQ257R, or the kinase-inactivating BRAFG596V, and treated with 0.1 μM PD0325901 or B. 1.0 μM PD0325901 from 4 hpf until 4 dpf. Zebrafish were imaged at the indicated developmental time postfertilization. The numbers of embryos displaying the presented phenotype are indicated. |