- Title
-
High-throughput screening of Australian marine organism extracts for bioactive molecules affecting the cellular storage of neutral lipids
- Authors
- Rae, J., Fontaine, F., Salim, A.A., Lo, H.P., Capon, R.J., Parton, R.G., and Martin, S.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
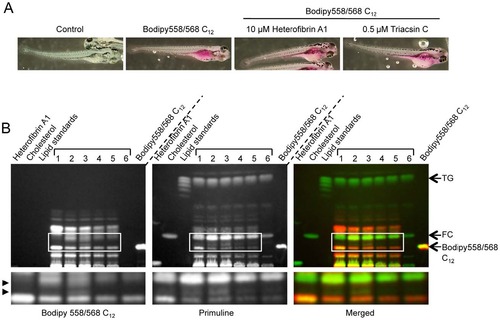
Metabolism of fluorescent fatty acid in zebrafish embryos. Zebrafish embryos (day 4–6 post-fertilisation) were incubated in the presence or absence of 10 μM heterofibrin A1 or 0.5 µM triacsin C for 2 h prior to the addition of Bodipy558/568 C12 for 6 h. Control embryos were incubated with vehicle (DMSO) only. Embryos were subsequently processed for fluorescence microscopy or TLC. (A) Embryos were fixed and fluorescent fatty acid imaged using a stereo dissecting microscope. (B) Embryos were homogenised, neutral lipids extracted and resolved using TLC. Total lipids were visualised using primuline and metabolised Bodipy558/568 C12 was detected by intrinsic fluorescence. The treatments were as follows: Lane 1, 0.5 μM triacsin C + Bodipy 558/568 C12; lane 2, 5 μM heterofibrin A1 + Bodipy 558/568 C12; lane 3, 10 μM heterofibrin A1 + Bodipy 558/568 C12; lane 4, Bodipy 558/568 C12; lane 5, DMSO + Bodipy 558/568 C12; lane 6 no treatment. Control lanes contained 65 μg heterofibrin A1, 10 μg cholesterol, 45 μg lipid standards and 24 µg Bodipy558/568 C12. Arrows delineate triglycerides (TG), free cholesterol (FC) and Bodipy558/568 C12. Arrowheads indicate Bodipy558/568 C12 metabolites accumulated in embryos in the presence of heterofibrin A1. Lower panels highlight regions of the TLC plate incorporating novel metabolites. |