- Title
-
The Prx1 limb enhancers: Targeted gene expression in developing zebrafish pectoral fins
- Authors
- Hernández-Vega, A., and Minguillón, C.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
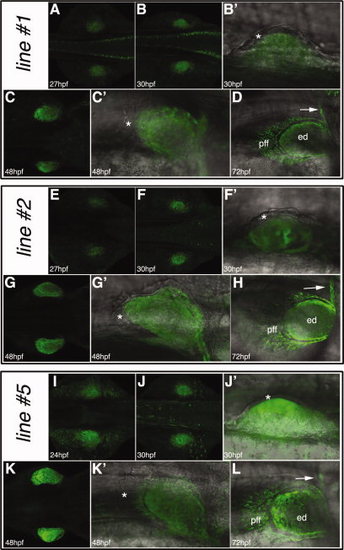
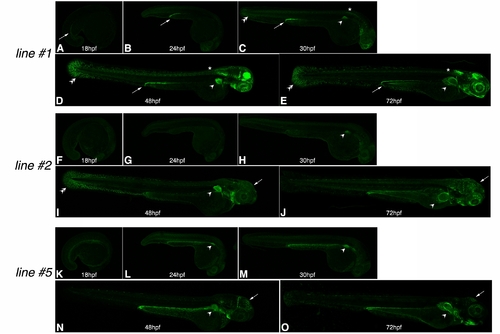
The mPrx1(cFos):EGFP transgenic lines. A–D: The mPrx1(cFos):EGFP reporter line#1. E–H: The mPrx1(cFos):EGFP line#2. I–L: The mPrx1(cFos):EGFP line#5. For all the embryos dorsal views are shown with anterior to the right, whereas lateral views with anterior to the right are shown for the fin bud details. The asterisks mark lack of enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) expression in the fin ectoderm and the arrows the scapulocoracoid. ed, endoskeletal disc; pff, pectoral fin fold. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
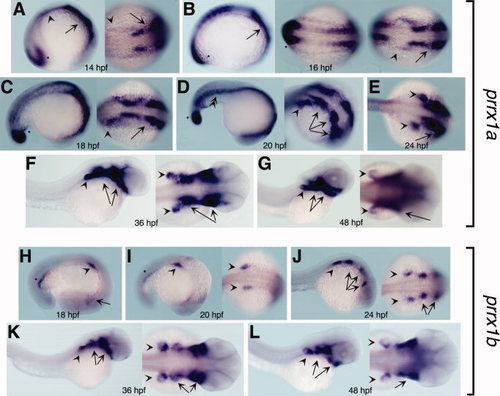
Expression patterns of the zebrafish prrx1a and prrx1b genes. A–G:prrx1a expression from 14 to 48 hpf. The asterisk denotes expression in the tail bud, the arrowhead in the LPM first and pectoral fins later, the arrow in the head mesenchyme first and branchial arches later and the double-arrowhead in the ventral part of the somites. H–L:prrx1b expression from 18 to 48 hours postfertilization (hpf). The asterisk denotes pronephric ducts, the arrowhead pectoral fins and the arrows expression in the branchial arches. All the embryos are oriented with anterior to the right. Lateral views are shown for the images at the left whereas dorsal ones are presented in middle or right images. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
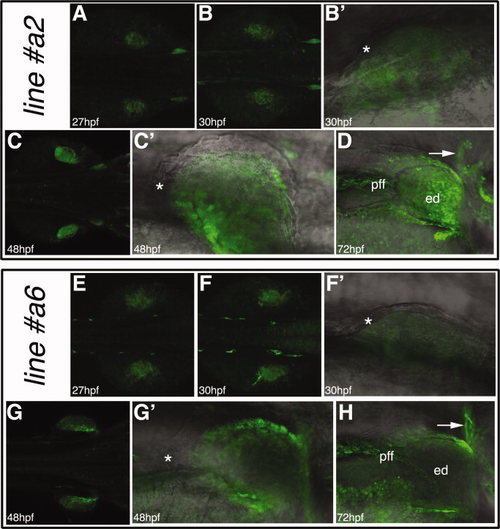
The zfprrx1aCNE (cFos):EGFP transgenic lines. A–D: The zfprrx1aCNE(cFos):EGFP reporter line#2. E–H: The zfprrx1aCNE(cFos):EGFP line#6. For all the embryos, dorsal views are shown with anterior to the right, whereas lateral views with anterior to the right are shown for the fin bud details. The asterisks mark the unlabelled fin ectoderm and the arrows the scapulocoracoid. EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; ed, endoskeletal disc; pff, pectoral fin fold. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
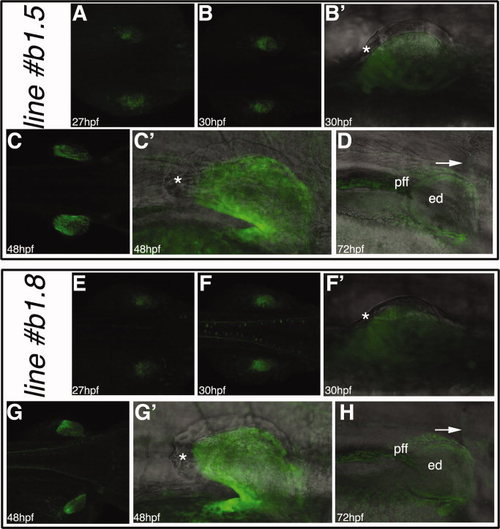
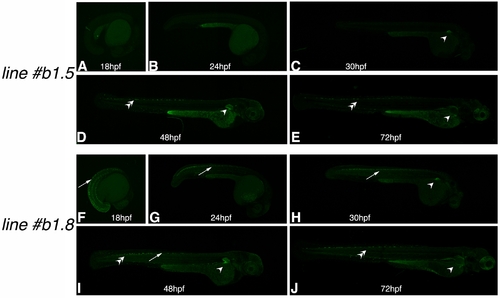
The zfprrx1b1CNE(cFos):EGFP transgenic lines. A–D: The zfprrx1b1CNE(cFos):EGFP reporter line#5. E–H: The zfprrx1b1CNE(cFos):EGFP line#8. For all the embryos, dorsal views are shown with anterior to the right, whereas lateral views with anterior to the right are shown for the fin bud details. The asterisks mark the unlabeled fin ectoderm and the arrows the scapulocoracoid. EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; ed, endoskeletal disc; pff, pectoral fin fold. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
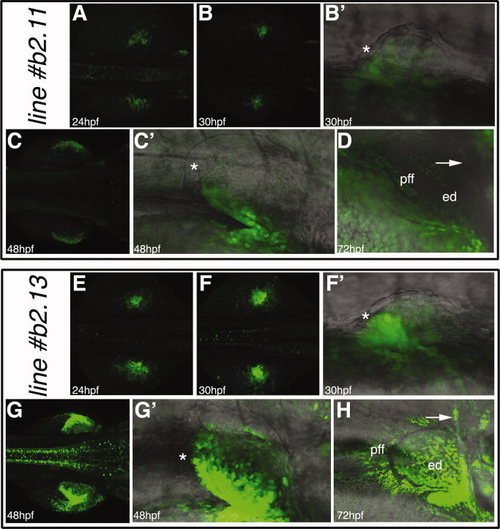
The zfprrx1b2CNE(cFos):EGFP transgenic lines. A–D: The zfprrx1b2CNE(cFos):EGFP reporter line#11. E–H: The zfprrx1b2CNE(cFos):EGFP line#13. For all the embryos, dorsal views are shown with anterior to the right, whereas lateral views with anterior to the right are shown for the fin bud details. The asterisks mark the unlabelled fin ectoderm and the arrows the scapulocoracoid. ed, endoskeletal disc; pff, pectoral fin fold. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
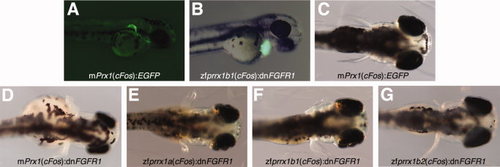
Interferring with FGFR1 function in the developing pectoral fins. A: A 48 hours postfertilization (hpf) control embryo injected with the mPrx1(cFos):EGFP construct showing high reporter expression in the pectoral fins. B: A 48 hpf injected embryo showing high expression of EGFP in the heart. C: Lack of fin phenotype after injection of the mPrx1(cFos):EGFP construct. D–G: Range of fin phenotypes obtained after injection of the mPrx1(cFos):dnFGFR1 (D), zfprrx1a(cFos):dnFGFR1 (E), zfprrx1b1(cFos):dnFGFR1 (F) and zfprrx1b2(cFos):dnFGFR1 (G) constructs. A and B are lateral views of 48 hpf embryos with anterior to the right, whereas C–G are dorsal views of 4 dpf larvi with anterior to the right. |
|
Analysis of reporter gene expression in other tissues than the pectoral fins: the mPrx1(cFos):EGFP lines. A–E: mPrx1(cFos):EGFP line#1. Apart from the expression in the developing pectoral fins from 27 hours postfertilization (hpf)onwards (marked here by arrowheads in C–E), enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) signal is observed in the following territories: (i) In the pronephric duct from 18 hpf (arrows in A–E). (ii) From 30 hpf, EGFP labels some mesenchymal cells in the median fin fold (double arrowheads in C–E). (iii) Some cells of the spinal cord at the level of the pectoral fin from 27 hpf onward (asterisks in C–E and Fig. 2 A, B). (iv) From 48 hpf, expression of EGFP is observed in anterior brain and retina. F–J: mPrx1(cFos):EGFP line#2. Apart from the expression in the developing pectoral fins from 27 hpf onward (marked here by arrowheads in H–J), EGFP signal is observed in the following areas: (i) At 48 hpf, EGFP labels some mesenchymal cells in the median fin fold (double arrowheads in I) and (ii) in mesenchymal cells in the dorsal aspect of the head at 48 and 72 hpf (arrows in I, J). K–O: mPrx1(cFos):EGFP line#5. Apart from the expression in the developing pectoral fins from 24 hpf onward (marked by arrowheads in L–O), EGFP signal is also observed in a dorsal cranial bone of the 48 and 72 hpf embryos marked by arrows in N and O. Specific sites of reporter gene expression (other than the limb) in each of the transgenic lines generated may represent positional effects due to different integration sites of the transgene. Reporter gene expression is also detected in areas of the ventral head mesenchyme in all the transgenic lines created which is a characteristic of the mPrx1 limb element (Logan et al., 2002). Nonspecific expression in the dorsal-most aspect of the yolk extension is observed in all three transgenic lines (A–O). |
|
Analysis of reporter gene expression in other tissues than the pectoral fins: the zfprrx1aCNE:EGFP lines. A–E: zfprrx1a(cFos):EGFP line#2. Apart from the expression in the developing pectoral fins from 27 hours postfertilization (hpf) onward (marked by arrowheads in C–E), enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) signal is observed in (i) part of the somites of the 18 hpf embryo (so, in A) and in (ii) the otic vesicle and anterior lateral line from 24 hpf onward (arrows in B–E and Fig. 5 A–C). F–J: zfprrx1a(cFos):EGFP line#6. Apart from the expression in the developing pectoral fins from 27 hpf onward (marked here by arrowheads in H–J), EGFP signal is also observed in the anterior brain and retina from 24 hpf onward (arrows in G–J). The specific sites of reporter gene expression in each of the transgenic lines may represent positional effects due to different integration sites of the transgene. Reporter gene expression is also detected in common areas in the two transgenic lines, which are some mesenchymal cells in the median fin fold and scattered cells surrounding the somatic tissue (mff and double arrowheads(Logan et al., 2002). Nonspecific expression in the dorsal-most aspect of the yolk extension is observed in these transgenic lines (A–J). |
|
Analysis of reporter gene expression in other tissues than the pectoral fins: the zfprrx1b1CNE:EGFP lines. A–E: zfprrx1b1(cFos):EGFP line#5. Expression in this transgenic line is very pectoral fin-specific until at least 30 hours postfertilization (hpf; Fig. 6 and C here). F–J: zfprrx1b1(cFos):EGFP line#8. Apart from the expression in the developing pectoral fins from 27 hpf onward (marked here by arrowheads in H–J), enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) signal is also observed in some cells of the spinal cord from 18 to 48 hpf (arrows in F–I). Because this expression site is not observed in the other transgenic line generated by injection of the same DNA construct (zfprrx1b1(cFos):EGFP line#5), it is most probably due to a positional effect. Similar to the expression observed in the zfprrx1aCNE:EGFP lines EGFP signal is also observed in scattered cells surrounding the somatic muscles at 48 and 72 hpf (double arrows in D, E and I, J), suggesting these represent true expression sites driven by the orthologous enhancers zfprrx1a and zfprrx1b1 CNEs. Again, nonspecific expression in the yolk extension is observed (A–J). |
|
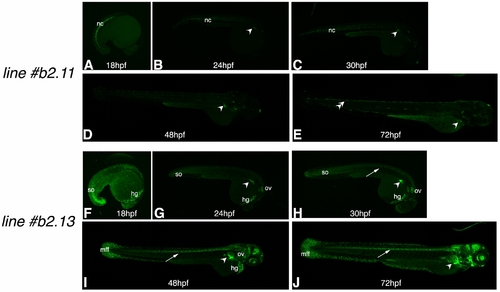
Analysis of reporter gene expression in other tissues than the pectoral fins: the zfprrx1b2CNE:EGFP lines. A–E: zfprrx1b2(cFos):EGFP line#11. Apart from the expression in the developing pectoral fins from 24 hours postfertilization (hpf)onward (marked by arrowheads in B–E), detectable enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) signal is observed in (i) the notochord from 18 to 30 hpf (nc, A–C) and in scattered cells surrounding the somatic muscles at 72 hpf (double arrows in E). F–J: zfprrx1b2(cFos):EGFP line#13. Apart from the expression in the developing pectoral fins from 24 hpf onward (marked here by arrowheads in G–J), EGFP signal is also observed in the following territories: (i) in the posterior-most somites from 18 to 30 hpf (so, F–H), (ii) in the hatching gland from 18 hpf onward (hg, F–I), (iii) in the otic vesicle from 24 hpf onward (ov, G–I), (iv) in the spinal cord from 30 hpf (arrows in H–J) and (v) in the anterior brain and retina as well as mesenchymal cells of the medial fin fold of the 48 and 72 hpf embryos (mff, I, J). The specific sites of reporter gene expression in the transgenic lines reported here represent positional effects due to different integration sites of the transgene. Nonspecific expression in the dorsal-most aspect of the yolk extension is also observed in these transgenic lines (A–J). All the images shown in Supp. Figs. 1S–S4 have been enhanced (as a whole) to make EGFP expression in other sites than the fins clearly observable. |
|
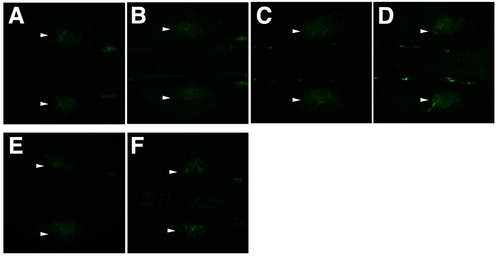
Original images with the same settings as those used for Figure 2. A: zfprrx1a CNE line#2 27 hpf embryo. B: zfprrx1a CNE line#2 30 hpf embryo. C: zfprrx1a CNE line#6 27 hpf embryo. D: zfprrx1a CNE line#6 30 hpf embryo. E: zfprrx1b1 CNE line#5 27 hpf embryo. F: zfprrx1b2 CNE line#11 24 hpf embryo. Expression in the pectoral fins is marked by arrowheads. |

Unillustrated author statements |