- Title
-
Identification of cis regulatory features in the embryonic zebrafish genome through large-scale profiling of H3K4me1 and H3K4me3 binding sites
- Authors
- Aday, A.W., Zhu, L.J., Lakshmanan, A., Wang, J., and Lawson, N.D.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
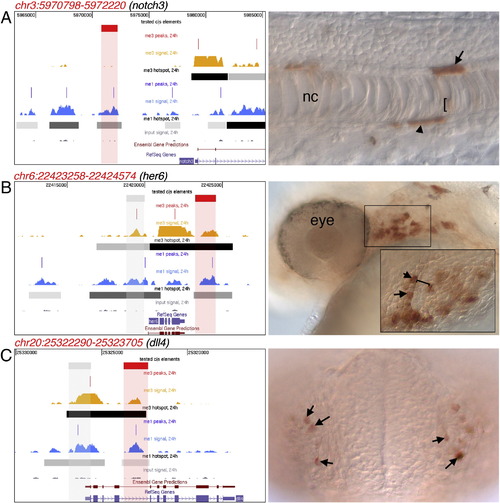
H3K4me1-positive elements can be active enhancers in zebrafish embryos. A. Left, genomic region upstream of notch3 showing location of H3K4me1-positive element (in red) used for reporter assay. Right, expression of Egfp driven by enhancer element shown at left in hypochord (arrow), floor plate (arrowhead), and lower levels in the notochord (nc, low-level positive cells indicated by bracket); lateral view, dorsal is up, anterior to the left. B. Left, genomic region upstream of her6 showing location of H3K4me1-positive elements used for reporter assay; red and gray boxes indicate element that drove or did not drive expression, respectively. Right, expression of Egfp driven by the active enhancer element shown at left in region of the pharyngeal arches (boxed area); inset, higher magnification of pharyngeal arch region showing positive mesenchymal surrounding the arch (bracket); images are not from the same embryo lateral view, dorsal is up, anterior to the left. C. Left, genomic region upstream of dll4 showing location of H3K4me1-positive element used for reporter assay. Red and gray boxes indicate element that drove or did not drive expression, respectively. Right, expression of Egfp driven by active enhancer element shown at left in cells residing in the olfactory placode (arrows); frontal view, dorsal is up. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 357(2), Aday, A.W., Zhu, L.J., Lakshmanan, A., Wang, J., and Lawson, N.D., Identification of cis regulatory features in the embryonic zebrafish genome through large-scale profiling of H3K4me1 and H3K4me3 binding sites, 450-62, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.