- Title
-
Nephroprotective Role of Resveratrol and Ursolic Acid in Aristolochic Acid Intoxicated Zebrafish
- Authors
- Ding, Y.J., Sun, C.Y., Wen, C.C., Chen, Y.H.
- Source
- Full text @ Toxins (Basel)
|
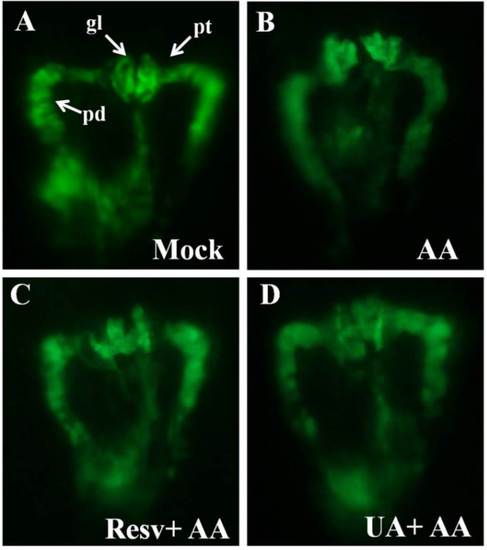
Kidney phenotypes of zebrafish embryos after prevention (10 ppm Resv or UA). (A) No defect of mock group; (B) AA caused atrophic glomerulus and pronephric tube (pt) curved defect; (C and D) Prevention groups treated to restore a similar phenotype as the mock group. All kidney photos were taken from the dorsal view at the developmental stage of 48 hpf. Tg(wt1b:EGFP). pt, pronephric tubule; pd, pronephric duct; gl, glomerulus; (E,F) The Tukey-Kramer HSD (honestly significant difference) test: the mean malformation rates and their 95% confidence intervals for treatment groups. Two group means were considered significantly different if their intervals were disjointed and were not significantly different if their intervals overlapped. |
|
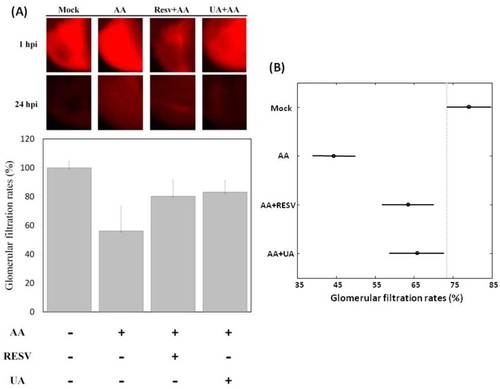
Glomerular filtration rates of Resv and UA prevent aristolochic acid nephropathy (AAN). (A) Zebrafish embryos were either exposed to water (no treatment) or water containing 5 ppm AA and 10 ppm Resv or UA exposure. Dextran tetramethylrhodamine was injected into the cardiac venous sinus of 72 hpf embryos derived from different groups (mock, prevention), and fluorescence intensities were recorded after 1 h post-injection (hpi) and 24 hpi (n = 15); (B) Tukey-Kramer HSD test: the mean glomerular filtration rates and their 95% confidence intervals for treatment groups (“Mock”, “AA “, “AA+Resv”, and “AA+UA”). Two group means were considered to be significantly different if their intervals were disjointed and were not significantly different if their intervals overlapped. |
|
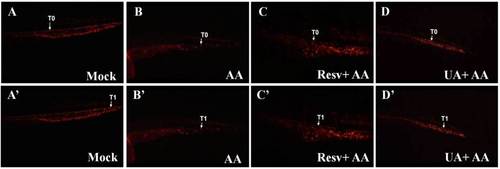
Effects of Resv or UA on blood circulation. Images were captured by live video (Supplementary movie S1) of Tg(gata1:DsRed) embryos without AA treatment (A,A′) after 3 ppm AA treatment (B,B′) and Resv or UA prevention groups (C,C′,D,D′). T0: Initial position of one red blood cell; T1: Position of the red blood cell 1 s later. |
|
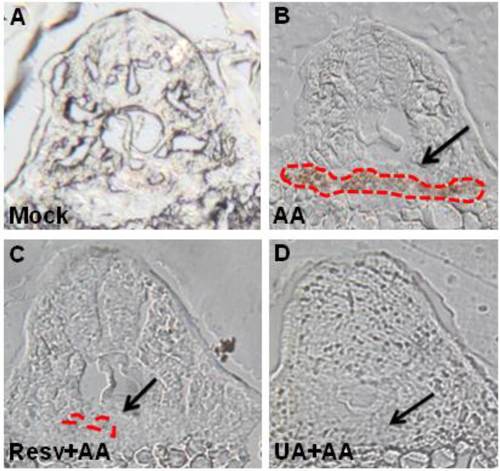
Resv or UA decrease AA-induced red blood cell accumulation. Embryos derived from the mock (no treatment: A), AA-treated group (B), and Resv (C) or UA prevention groups (D) were stained with o-dianisidine. The black arrow indicates the position of the glomerulus. The red dots indicate the region of blood accumulation. |