- Title
-
A Gal4/UAS system for conditional transgene expression in rhombomere 4 of the zebrafish hindbrain
- Authors
- Choe, S.K., Nakamura, M., Ladam, F., Etheridge, L., and Sagerström, C.G.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
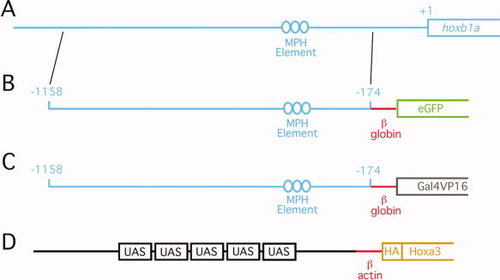
Diagram of transgenic constructs. A: Genomic DNA between positions 1,158 and 174 (relative to translation start site) was isolated from the zebrafish hoxb1a locus. This sequence was cloned upstream of the murine βglobin promoter and used to drive eGFP (B) or Gal4VP16 (C). D: Five UAS elements were cloned upstream of the carp β-actin promoter and used to drive HA-tagged hoxa3a. See Experimental Procedures section for specific details of transgene construction. “MPH element” indicates the position of previously defined Meis/Pbx/Hox binding sites required for r4-restricted expression of the hoxb1a gene. |
|
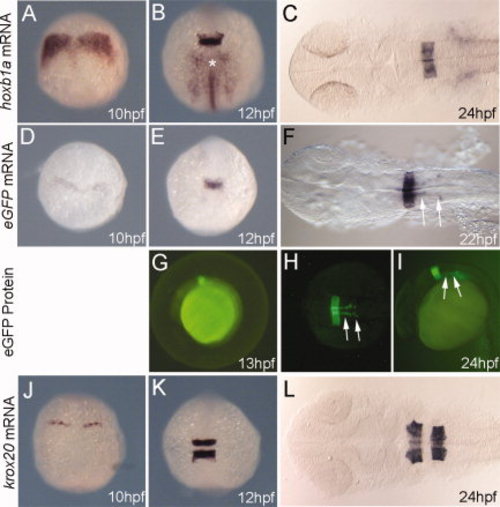
hoxb1a(β-globin):eGFPum8 transgenic embryos express GFP in r4, but are otherwise indistinguishable from non-transgenic siblings. Embryos were collected at the indicated stages and assayed for expression of hoxb1a (A–C), eGFP (D–F), or krox20 (J–L) by in situ hybridization as well as for eGFP fluorescence (G–I). All embryos are from an outcross of a heterozygous hoxb1a(β-globin):eGFPum8 carrier. Embryos in D–I are heterozygous for the hoxb1a(β-globin):eGFPum8 transgene. Embryos in A–C and J–L may be either heterozygous or non-transgenic, but there is no difference in expression of hoxb1a and krox20 within the clutch of embryos. Asterisk in B indicates hoxb1a expression in mesoderm. Arrows in F, H, I indicate eGFP expression in migrating nVII facial motor neurons. All embryos are in dorsal view except G and I, which are lateral views. Anterior is to the top (A, B, D, E, J, K) or to the left (C, F, G, H, I, L). |
|
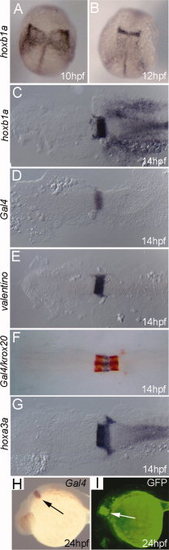
Transgenic embryos from the hoxb1a(β-globin):Gal4VP16um60 line are indistinguishable from their non-transgenic siblings with respect to expression of all hindbrain genes tested. Embryos were collected at the indicated stages and assayed for expression of hoxb1a (A–C), Gal4 (D, F, H), valentino (E), krox20 (F; detected in red), or hoxa3a (G) by in situ hybridization. I: hoxb1a(β-globin):Gal4VP16um60 embryos were injected with a 10× UAS:GFP plasmid and assayed for GFP fluorescence at 24hpf. All embryos are from an outcross of a heterozygous hoxb1a(β-globin):Gal4VP16um60 carrier. Embryos in D, F, H, I are heterozygous for the hoxb1a(β-globin):Gal4VP16um60 transgene while embryos in A–C, E, G may be either heterozygous or non-transgenic, but there is no difference in expression of hoxb1a, valentine, hoxa3a, or krox20 within the clutch of embryos. Arrows in H and I indicate expression in r4. A–G are dorsal views with anterior to the top (A, B) or the left (C–G). H and I are in lateral view with anterior to the left. |
|
UAS(β-actin):hoxa3aum61 transgenic embryos are indistinguishable from their non-transgenic siblings with respect to expression of all hindbrain genes tested. Embryos were collected at 14hpf and assayed for expression of hoxb1a (A), valentino (B), krox20 (C), or hoxa3a (D). All embryos are from an outcross of a heterozygous UAS(β-actin):hoxa3aum61 carrier and may be either heterozygous or wild type, but there is no difference in expression of hoxb1a, valentine, hoxa3a, and krox20 within the clutch of embryos. Embryos are in dorsal view with anterior to the left. |
|
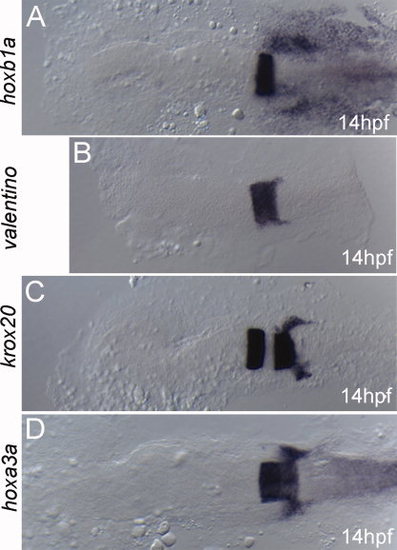
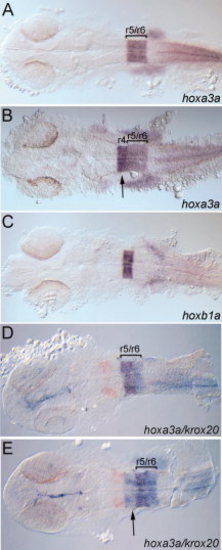
hoxb1a(β-globin):Gal4VP16um60 drives expression of the UAS(β-actin):hoxa3aum61 transgene in rhombomere 4. Embryos were collected at 24 hpf and assayed for expression of hoxa3a (A, B, D, E), hoxb1a (C), or krox20 (D, E; detected in red). All embryos are from a hoxb1a(β-globin):Gal4VP16um60 × UAS(β-actin):hoxa3aum61 cross. Embryos in B, E are double transgenic while embryos in A, C, D may be either single transgenic or wild type. Brackets in A, B, D, E delineate r5/r6. Arrows in B, E point to hoxa3a expression in r4. All embryos are in dorsal view with anterior to the left. |
|
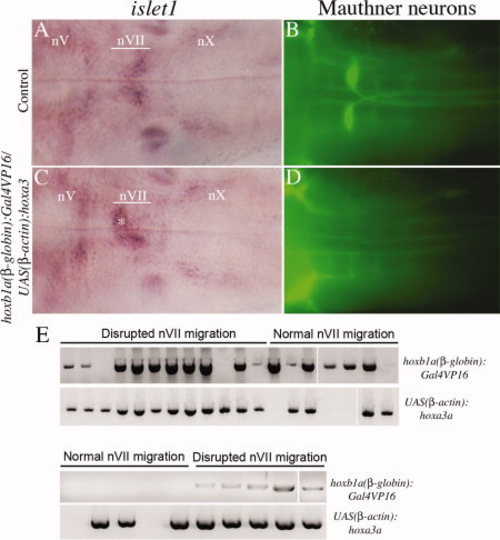
Characterization of embryos from a hoxb1a(β-globin):Gal4VP16um60/UAS(β-actin):hoxa3aum61 cross. Embryos were collected at 48 hpf and assayed for expression of islet1 to detect motor neurons (A, C) and 3A10 to detect Mauthner neurons (B, D). E: Embryos with normal or abnormal nVII migration were picked from two representative experiments and genotyped by PCR for the presence of the Gal4VP16 and the UAS:Hoxa3a transgene. nV, trigeminal motorneuron; nVII, facial motorneuron; nX, vagal motorneuron. Asterisk in C indicates nVII neurons remaining in r4. All embryos are in dorsal view with anterior to the left. |